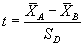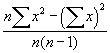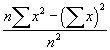Same - Determine if two numeric points are the same within a limit
Usage
| |
logical = Same ( num1 num2 epsilon tagarg ) |
| |
value = nSame ( arguments same as Same ) |
Parameters
| |
logical |
TRUE if the two arguments are the same within the limits of epsilon. |
| |
num1 |
The first numeric argument. |
| |
num2 |
The second numeric argument. |
| |
epsilon |
An optional upper limit by which the first two arguments can differ and still be considered the same. If this parameter is not specified then 0.005 is assumed. |
| |
tagarg |
Optional tagged arguments described below. |
Tagged Arguments
| |
Else::point |
Specifies the value to be returned if the first two arguments are not the same. |
| |
ElseIf::logical |
Continues an If/Else tag chain. |
| |
Then::point |
The value to be returned if the first two arguments are the same. |
Description
This module calculates the absolute value of the difference between the first two arguments. If that value is less than or equal to espilon then Logical:True is returned. Otherwise Logical:False is returned.
The nSame module is equivalent to {~Same()}.
Examples
| |
Same(1.1 1.2 0.1) |
returns Logical:True |
| |
Same(1.1 1.2 0.05) |
returns Logical:False |
Secure - Secure Subsets of V4
Usage
| |
result = Secure ( tagarg ) |
Parameters
| |
result |
The result of the module which varies according to the arguments |
| |
tagarg |
One or more tagged arguments described below |
Tagged Arguments
| |
AreaAll::logical |
If logical is TRUE then prevent execution of any of the area commands or modules. Returns the prior setting of this option. |
| |
AreaUpdate::logical |
If logical is TRUE then prevent execution of any of the area update commands or modules. Returns the prior setting of this option. |
| |
CPU::seconds |
This option causes V4 to terminate if its main process consumes more than seconds CPU seconds. See also the discussion below on V4 watchdogs. |
| |
Data::logical |
If TRUE then redirection of the DATA stream is not allowed. |
| |
Echo::logical |
If logical is TRUE then prevent execution of any of the echo commands or modules. Returns the prior setting of this option. |
| |
EvalNest::logical |
If logical is TRUE then prevent execution of any nested V4 evaluations (e.g. EvalCmd module). Returns the prior setting of this option. |
| |
Files::logical |
If logical is TRUE then prevent execution of any of the file access/update commands or modules. Returns the prior setting of this option. |
| |
Hidden::dimension |
Sets the 'hidden' flag for the dimension. The dimension will appear to be undefined (i.e. any reference will result in a 'Point not defined...' error. Furthermore, any future output of the dimension will be displayed with 'UV4:hidden'. This is identical to the Hidden option within the Dim module. |
| |
HTTPGet::quota |
Restricts the total number of bytes that subsequent HTTP calls may retrieve. |
| |
HTTPPut::quota |
Restricts the total number of bytes that subsequent HTTP calls may send/post. |
| |
Idle::minutes |
This option causes a V4 process to terminate if it goes for more than minutes without stdin input. See also the discussion below on V4 watchdogs. |
| |
Intersection::kiscts |
This option causes V4 to terminate after it has performed more than kiscts kilo-intersection evaluations. See also the discussion below on V4 watchdogs. |
| |
Key::value |
This option must be used in order to restore access to the Secure module. The value is the 64 bit key returned when the module was locked. |
| |
Lock::module |
Prevents future access to the V4 module. If the module is Secure then a 64 bit key is returned. This key must be given (see Key option above) to unlock the module. |
| |
Module::intmod |
Specifying an internal module (intmod) prevents any subsequent parsing of V4 source referencing the module. It does not prevent the subsequent execution of the module, only its reference. |
| |
OSFileInfo::logical |
If logical is TRUE then prevent execution of any of the OSFile information options. Returns the prior setting of this option. |
| |
OSFileListOf::logical |
If logical is TRUE then prevent execution of any of the OSFile ListOf options. Returns the prior setting of this option. |
| |
ProjectArea::logical |
If logical is TRUE then prevent creation of a Project Area file. Returns the prior setting of this option. |
| |
Redirection::logical |
If logical is TRUE then prevent execution of any of the output redirection options. Returns the prior setting of this option. |
| |
Test::logical |
If logical is true then prevent the use of the V4(Test) feature. |
| |
Unlock::module |
Unlocks (removes restrictions) on the specified V4 module. (See also Key for unlocking the Secure module.) |
| |
Value::section.name |
Returns the value associated with the named entry within the section within the v4site.ini file. See the discussion below. |
| |
XDBAccess::logical |
If logical is TRUE then prevent all read access to external databases (via DBGet module). Returns the prior setting of this option. Note that this differs from restricting the DBGet module. This restricts any subsequent access even with previously compiled bindings. |
| |
XDBXct::logical |
If logical is TRUE then prevent all updates to external databases (via DBXct module). Returns the prior setting of this option. |
Tagged Results
| |
AreaAll? |
Returns TRUE if all area command and modules are restricted, FALSE otherwise. |
| |
AreaUpdate? |
Returns TRUE if all area update commands and modules are restricted, FALSE otherwise. |
| |
Echo? |
Returns TRUE if all echo commands and modules are restricted, FALSE otherwise. |
| |
EvalNest? |
Returns TRUE if nested evaluations are restricted, FALSE otherwise. |
| |
Files? |
Returns TRUE if all file commands and modules are restricted, FALSE otherwise. |
| |
HTTPGet? |
Returns the restriction quota on HTTP calls. |
| |
HTTPPut? |
Returns the restriction quota on HTTP sends/posts. |
| |
OSFileInfo? |
Returns TRUE if all OSFile information tags are restricted, FALSE otherwise. |
| |
OSFileListOf? |
Returns TRUE if the OSFile ListOf operation is restricted, FALSE otherwise. |
| |
ProjectArea? |
Returns TRUE if the creation of a Project Area file is restricted, FALSE otherwise. |
| |
Redirection? |
Returns TRUE if all output redirection options are restricted, FALSE otherwise. |
| |
SessionKey? |
Generates a new 32 byte string that the V4 xlib package uses as a web session key. |
| |
Test? |
Returns the restriction status of the V4(Test) feature. |
| |
XDBAccess? |
Returns the restriction status of access to external databases. |
| |
XDBXct? |
Returns the restriction status of updates to external databases. |
Description
This module can be used to lock-down or restrict access to just about any feature within V4. This feature is to be used when a trusted process must link to to an untrusted (or undebugged) area of bindings and run potentially harmful code.
If the Secure module itself is restricted a 64-bit random key is returned. This key must be the first argument of any subsequent call to Secure or the module will fail. If an incorrect key is given, V4 will internally sleep for an unspecified amount of time. This delay effectively eliminates the possibility of a brut-force attempt to guess at the key.
There are three watchdog options within this module: CPU, Idle and Intersection. All three are implemented with the spawning of a watchdog subprocess. This process wakes up periodically and compares the current V4 environment with the limits currently in effect. If any of the limits have been exceeded then the main process is terminated. The wakeup interval of this watchdog is currently 10 seconds. This means that any limit will likely be exceeded before a V4 process is actually terminated. For example if the CPU limit is set at 60 seconds then it is possible that a process could consume almost 70 seconds before terminating.
Each time an instance of V4 is started it looks for a file v4runtimeinfo-majorversion-minorversion.bin in the v4 home directory. If the file does not exist it is created from the v4i files also in that home directory plus the v4site.ini file. This file contains any sensitive information that you need to run an application but don't want to explicitly reference within the V4 source code. The format of the file is similar to Window's ini files. It consists of sections and entries within the sections. Section names are enclosed in brackets and name=value entries appear on following lines.
Taking the example file below, V4(Secure::"gmail.password") would return 'topsecret'.
Example 40 - Example v4site.ini file
| |
# v4Site.ini - Site specific information
[mysql]
password=secret
[gmail]
defaultSender="V4 Moderator"
userName=v4mod@gmail.com
password=topsecret
host=smtp.gmail.com
[client1]
ftpUsername=fred
ftpPassword=ftpsecret
|
| |
Secure(Lock::GuiAlert Lock::GuiMsgBox) |
Prevent access to the two gui modules |
| |
BindQE([secKey] Secure(Lock::Secure)) |
Prevent access to the Secure() module and save key to unlock |
| |
Secure(Key::[secKey] Unlock::Secure) |
Restore access to the Secure() module |
| |
Secure(AreaAll::TRUE) |
Prevent access to all Area commands and modules |
Self - Return Argument as Value
Usage
| |
result = Self ( point ) |
| |
result = Self ( point dimension ) |
Parameters
| |
result |
The result of evaluating point. |
| |
point |
Any V4 point. |
Description
The Self module simply returns its single argument as its value. Its main use is with other modules where an intersection is required but a context point is needed.
If a second argument is given and is a dimension then the result is returned as a point on that dimension. If the second argument is given but it is not a dimension then it is ignored. Note that no conversions are performed, the dimension is simply updated. This option is primarily for preventing endless recursion in UV4:Acceptor and UV4:Displayer bindings (see example below).
| |
Self(Cus*) |
returns the current customer |
| |
Self(Plus(1 3)) |
Int:4 |
| |
Self(@Plus(1 3)) |
@Plus(1 3) |
| |
Self("now is" Dim:Int) |
Int:"now is" |
| |
Dim lastName Alpha Displayer |
define an Alpha dimension |
| |
[UV4:Displayer lastName..] Str(lastName* Capitalize?) |
will recurse into oblivion |
| |
[UV4:Displayer lastName..] Str(Self(lastName Dim:Alpha) Capitalize?) |
will evaluate properly |
| |
Self(UDate:1/1/07 Dim:D) |
returns D:1/1/07 |
| |
Self(UDate:1/1/07 Dim:Int) |
returns Udate:1/1/07 (second argument ignored) |
SendMail - Send Email
Usage
| |
result = SendMail ( tagargs ) |
Parameters
| |
result |
The module returns Logical:true if successful and fails otherwise. |
| |
tagargs |
One or more of the tagged arguments below. |
Tagged Arguments
| |
Attach::file |
Include the named file as an attachment. |
| |
Attach::list |
The list must contain two alpha elements. The first is the name of the file or stream to be attached. The second is the name to be associated with the attachment. See below for an example. |
| |
Attach::stream |
Attach the text that has been written to the output stream identified by stream. The name of the attachment will be 'attachment'. |
| |
CC::list |
Send a CC to each of the email addresses within the list. |
| |
CC::address |
Send a CC (carbon copy) to the specified address. |
| |
Connection::type |
How to connect to the email server. The type must be TLS (transport layer security, DEFAULT), PLAIN (unencrypted) or TRYTLS (attempts a TLS connection and degrades to PLAIN if necessary). |
| |
Format::type |
The format of the email. The type must be either TEXT or HTML. |
| |
From::name |
Who the email is from. The format for name is alias <emailaddress> |
| |
Host::address |
The ip address of the hosting email server. |
| |
HTML::text |
Include the text within the email as an HTML segment. |
| |
HTML::stream |
Include the text, as an HTML segment, that has been written to the output stream identified by stream. |
| |
Include::file |
Include the contents of file within the body of the text. |
| |
Include::stream |
Include the contents of the named stream into the email. |
| |
Name::text |
Associates text as the name of the next email segment. |
| |
Password::text |
Specifies the connection password to the email server. It is used with the User tag. |
| |
Port::num |
The connection port number to use if connecting to a non-standard email server. |
| |
Reply::email |
An email reply-to address. Normally a reply returns to the email address of the sender. This can be overridden with this tag. |
| |
Subject::text |
The subject line for the email. |
| |
Text::stream |
Include the text, as an text segment, that has been written to the output stream identified by stream. |
| |
Text::text |
Include the text within the email as a text-only segment. |
| |
To::list |
Send the email to each of the email addresses within the list. |
| |
To::address |
Send the email to the specified address. |
| |
Trace::logical |
Turn debug tracing on if logical is TRUE. |
| |
User::name |
The username to be used in connecting to the email server. |
Tagged Results
| |
HTML? |
Treat the next argument as text for an HTML segment. See also the Include tag. |
Description
This module constructs a (multi-part) email message, connects to a server and passes the message to the server. Various tag combinations can be used to send a variety of email types.
Examples
| |
SendMail(... Attach::("foo.txt" "instructions.txt")) |
Attach the contents of foo.txt but use instructions.txt as the name of the attachment within the email. |
| |
SendMail(... From::"John Doe <jdoe@moo.com>") |
The 'from' field on the email will show as John Doe with most email clients. |
| |
SendMail(... HTML? Include::"body.htm") |
Include the file body.htm as an HTML segment within the email. |
Example 41 - Sending an email from a file stream
| |
Output(Create::"email.tmp" Id::emailHTML)
Do(Out::emailHTML write to the stream)
/* Optional repeat above for stream emailText */
nDefQ(Parse(email* As::email) Then::EchoW("Invalid email address: " email*))
SendMail(Host::"smtp.gmail.com" /* Use gmail to send email */
From::"V4 Documentation <v4@mksinc.com>"
User::Secure(Value::"email.userName") /* Pull the gmail user account name from the v4site.ini file */
Password::Secure(Value::"email.password")
Reply::[defaultReplyTo],UV4:none /* If we have a reply-to defined use it otherwise ignore */
Text? Include::Output(Id::emailText Close?),UV4:none /* If the emailText stream is defined then close it and use contents for text-only segment of email */
HTML? Include::Output(Id::emailHTML Close?))
|
Example 42 - Sending an email from a buffered stream
| |
Output(Buffered? Id::bufStream)
Do(Out::bufStream write to the stream)
SendMail(Host::"smtp.gmail.com" /* Use gmail to send email */
From::"V4 Documentation <v4@mksinc.com>"
User::Secure(Value::"email.userName") /* Pull the gmail user account name from the v4site.ini file */
Password::Secure(Value::"email.password")
Reply::[defaultReplyTo],UV4:none /* If we have a reply-to defined use it otherwise ignore */
Text? Include::bufStream))
Output(Id::bufStream Close?)
|
Socket - Send and Receive Data Through an Internet Socket
Usage
| |
result = Socket ( tagargs ) |
Parameters
| |
result |
The received data as a point on Dim:Alpha or Logical:True if no data is requested. |
| |
tagargs |
One or more of the tagged arguments below. |
Tagged Arguments
| |
Bytes::num |
Specifies the number of bytes to receive for the reply. |
| |
Close::logical |
Determines whether or not to close the socket connection. If Close:FALSE is given then the socket is not closed and remains open for subsequent Socket calls. The default is Close:TRUE. |
| |
Create::file |
The return message is written to file rather than returned as a V4 string. See also the Text option. |
| |
Echo::how |
This option is used for debugging. If how is SEND then all data sent through the socket is echoed to the current trace stream (see Output). If how is RECEIVE then all data received is echoed to the current trace stream. If how is ALL then both send and receive data is echoed. |
| |
Host::name |
The name of the server/host to connect to. This may be an entry in the local hosts file, an explicit IP address, or a domain name (e.g. www.mksinc.com). If no Host argument is given then the module fails unless a prior Socket call has been given with Close:FALSE. |
| |
Include::stream |
Same as Include:text except that the data is taken from the specified stream's output buffer. |
| |
Include::file |
Send the contents of file through the socket connection. If both a Message and Include arguments are given then the message text will be sent first and the file second. |
| |
Message::string |
The string is sent as the message to the target host/server. If no Message argument is given then no message is sent to the target. |
| |
Port::num |
The port number on the server to connect to. Like the Host argument, this is mandatory unless a prior Socket call has been given. |
| |
Reply::logical |
Determines whether or not the module receives a reply. The default is Reply:TRUE. |
| |
Session::mode |
Starts or completes a multi-Socket session. The mode should be OPEN to start a session and CLOSE to terminate a session. All attributes set when the session is open are carried across the subsequent Socket calls until the CLOSE is given. All input received on the socket connection is buffered and returned as a single Dim:Alpha point. |
| |
Text::logical |
This is used in conjunction with the Create option to specify if a text or binary file is created. The default value is TRUE (for text). |
| |
Until::num |
The module receives a reply until a byte equal to num is received. The default is Until:26 (ASCII EOM). |
| |
Until::string |
The module receives a reply until the string is matched in the reply. |
| |
Wait::seconds |
Specifies the maximum number of seconds to wait for a response. The default is 30 seconds. |
Description
This module is used to initiate a socket connection to a remote server, send a message to it, and optionally receive a reply. There is no implicit end-of-message with socket streams so either a length or terminating byte/string must be specified or the module will time/error out. The maximum length of a reply is limited to that of a V4 BigText point. Longer replies must be broken into multiple segments with several Socket calls OR through the use of the Create option to have the reply written to a file.
Only one socket connection can be made at a time. Multiple concurrent connections are not yet supported.
Examples
| |
Socket(Host::Remote123 Port:2001 Message::"now is the time") |
sends the message to host Remote123 on port 2001 and returns the reply as a point on the Alpha dimension |
Sort - Sort a List of Points
Usage
| |
sorted = Sort ( list sortoptions... ) |
Parameters
| |
sorted |
The sorted points of list. |
| |
list |
The list of points to be sorted. |
| |
sortoptions |
One or more intersections specifying how list is to be sorted. If just a quoted intersection is specified then ascending order is assumed. If the Reverse tag is used then reverse order is assumed. The By tag may be used for ascending sort order. |
Tagged Arguments
| |
By::isct |
Sort the points in list in ascending order by the value returned by evaluating isct for each point in the list. Multiple By's may be given for complex sorts. Caution - make sure that the results of evaluating isct for all points to be sorted result in the same type of value. This can easily happen where the default value of an intersection is different than the normal result. |
| |
Context::point |
For each enumeration point, V4 evaluates and inserts the point into the current context. If the point is UV4:none then nothing is done (i.e. UV4:none is not placed into the context). This point can be inserted into the context by quoting it: Context::@UV4:none. If point is UV4:Skip the current point is ignored entirely. |
| |
ContextP::point |
This is identical to the Context tag except that if point evaluates to a list then each point in the list is inserted into the context. |
| |
Do::isct |
After sorting the points in list, put each point in the current context and evaluate isct. This is equivalent to Enum(Sort(...) @isct) but more efficient because Sort does not have to generate an output list. Note that no list is returned by Sort. |
| |
Duplicate::logpt |
If logpt is TRUE then allow duplicate points in result (this is the default), otherwise remove duplicate points. |
| |
If::isct |
Test each point in list by evaluating isct. If isct returns true then include the point for sorting. If isct returns false then do not include the point. |
| |
Index::dim |
The dimension is inserted into the context with each selected point with an integer value representing the ordinal number of the point (i.e. the first selected point is reflected as dim:1, the second as 2, etc.) |
| |
Index::point |
The point is inserted into the context and incremented by one after each point. This allows one to specify a starting value for an index. |
| |
Num::number |
After sorting, only the first number points are returned. |
| |
Parent::pt |
Specifies the parent point. See Enum for a complete description. |
| |
PIf::isct |
Specifies a test based on the parent. See Enum for a complete description. |
| |
Reverse::isct |
Similar to By except that the points are sorted in descending order. |
| |
Shell::dim |
Each point in the list is added to the current context under dimension dim. Note that this dimension should be a shell dimension and should be specified as Dim:dim. When this argument is given the enumerating point is NOT added to the context under its own dimension. |
| |
Sum::isct |
Maintains a rolling sum of the isct. See Enum for a complete description. |
| |
While::isct |
Test each point in list by evaluating isct. If isct returns true then include the point for sorting. If isct returns false then that point and all other points in the list are not sorted- only those before the first evaluation of false. |
Tagged Results
| |
Pop? |
When this tag is specified, V4 will pop off the context frame after processing each point in the enumeration. This option should be considered if points of differing dimensions are being enumerated. In this case, a point may unknowingly remain in the context and the Pop? option is the only way to ensure that a single enumeration point resides in the context at a time. |
Description
The Sort module sorts its first argument list by the one or more sortoptions. Each sort option is an intersection usually referencing the points in list. By default the sort order is ascending.
Examples
| |
Sort(Cus.. By::Cus.State Reverse::Cus.AnnualSales ) |
Sort all points on Cus(tomer) dimension by state and descending annual sales |
| |
Sort(Cus.. Reverse::Cus.YTDSales Num::1) |
Sort customers by descending YTDSales and returns the first |
| |
Enum(Sort(IM.. If::{IM.Code = Code:xyz} By::IM.Id Do::EchoT(IM.Id IM.Description IM.Price))) |
Sorts all items having Code:xyz by Id and then outputs a table with the id, description, and price. |
| |
Sort(Item.. If::{Item.Code = Code:xyz} By::Item.Id Do::EchoT(Item.Id Item.Description Item.Price)) |
Same as the prior example |
Spawn - Invokes a Sub Process
Usage
| |
logical = Spawn ( command tags ) |
Parameters
| |
command |
A string argument to be executed. Multiple arguments are concatenated into a single command argument. |
| |
oshandle |
An OSHandle point referencing a previously created subprocess. |
| |
tags |
Any of the optional tags below. |
Tagged Arguments
| |
Active::oshpnt |
Returns Logical:True if the subprocess/thread oshpnt is currently active. The module fails if the subprocess/thread is no longer active. |
| |
Append::file |
All stdout/stderr output from the subprocess is append to the file. The file is created if necessary. The file is closed when the process terminates. |
| |
Arg::argstr |
Use argstr as the arguments. If not specified then then any arguments are assumed to be appended to the command line. |
| |
Bytes::max |
Limits the output of the spawned process to max bytes. The default is 10mb. |
| |
Create::file |
The file is created and all stdout/stderr output from the subprocess is sent to the file. The file is automatically closed when the process finishes or is terminated. |
| |
Echo::logical |
If TRUE then echo the command line to the status output stream before spawning the subprocess. |
| |
Echo::option |
If option is ONLY then only echo the command line. NO subprocess is spawned. This is a debugging option. |
| |
Maximum::secs |
V4 will wait a maximum of secs for the subprocess to complete. This applies to processes with Wait:TRUE or Wait:FALSE. |
| |
Result::oshpnt |
Returns the exit code of the specified subprocess/thread. If the process is still running then the module fails. |
| |
Wait::logical |
If logical is TRUE then wait for the subprocess to complete (default). If it is FALSE then spawn the process and immediately continue with V4 execution. If it is APPLICATION then the subprocess is spawned as an independent application. This option may also be used to wait for one or more previously created subprocesses with ALL or ANY. ALL waits for all subprocesses to complete, ANY for any one process to complete. |
Tagged Results
| |
Echo? |
Echo the command line to the status output stream. The line is output immediately before the subprocess is created. |
Description
The Spawn module invokes a sub process and passes the command string to be executed by the sub process. The format of the command string may vary across operating systems.
Examples
| |
Spawn("cmd /C del *.foo") |
Deletes files (under Windows) |
| |
[DelCommand] "cmd /C del " |
Bind value to intersection |
| |
Spawn([DelCommand] "*.foo") |
same as above |
| |
BindQE([Proc1] Spawn("program1" Wait::No)) |
Starts program1 and binds [Proc1] to the process point |
| |
BindQE([Proc2] Spawn("program2" Wait::No)) |
Starts program2 and binds [Proc2] to the process point |
| |
Spawn([Proc1] [Proc2] Wait::All) |
Waits for both program1 and program2 to complete |
| |
Spawn([Proc1] [Proc2] Wait::Any) |
Waits for either program1 or program2 to complete |
Sqrt - Calculate the Square Root
Usage
Parameters
| |
result |
The resulting square root |
| |
number |
The number to calculate the square root of |
Description
The Sqrt module calculates the square root of its argument.
SSDim - Set SpreadSheet Options for Dimension
Usage
| |
undef = SSDim ( Dim:dim pt1 pt2 ... ) |
Parameters
| |
dim |
The dimension to be set (or special keyword). |
| |
pt1 |
An option to be set for the dimension. |
Tagged Arguments
| |
CellColor::name |
The color of the spreadsheet cell. Colors may be specified as a 24 hexadecimal number of the form #rrggbb or as any valid HTML color. |
| |
Class::name |
Associate the CSS class name with the dimension. |
| |
CSS::string |
Associate the cascading style sheet attributes in string with the dimension. |
| |
Font::name |
Associates the spreadsheet font name to the dimension. |
| |
FontSize::npt |
Associates a font size to the dimension. The value can be a integer from 1 to 256, or a percentage from 0 to 256%. |
| |
Id::name |
Associate the CSS Id name with the dimension. |
| |
Mask::string |
Associates an output format mask (ex: 0,000.00) to a dimension. |
| |
Position::list |
Defines absolute positioning characteristics for the current table or sheet. The elements of the list are combinations of the following tagged values: Height to specify the height of the table, Left to give the left starting position, Right for the rightmost position, Top for the top of the table, and Width for the width. |
| |
Style::tagOption |
Associates a set of format options to the dimension. The supported options are described in the table below. |
| |
StyleName::tagOption |
Associates a spreadsheet style name to a dimension. |
| |
TextColor::tagOption |
Specifies the color of the text. The name is the same as the CellColor tag. |
| |
URL::urlspec |
A URL to be associated with points on this dimension. Each point on this dimension will be hyperlinked via urlspec upon conversion to HTML. The xvrestohtml process will scan urlspec for the asterisk character and when found will substitute it with the current text value of the dimension point. This option is often used with the Include tag within the EchoS module. |
| |
Width::num |
Specifies the width of a column. If num is a number between 0 and 1 (e.g. 0.15) then it is taken as a percentage of the screen width. If it is an integer number greater than 1 then it is considered to be pixels. This option only applies to HTML output. |
Tagged Results
| |
CSS? |
Convert the formatting associated with the prior dimension to Cascading Style Sheet format. |
| |
Mask? |
Returns the formatting mask (set with the Format tag) for the dimension. The module fails if no format mask has been set for the dimension. |
Description
The SSDim module associates one or more spreadsheet formatting attributes to a dimension. When points on the dimension are sent to a spreadsheet via EchoS, the cells receiving the points are appropriately formatted. Multiple dimensions can be specified within a single module call.
This module usually associates formatting with a dimension. It may also associate formatting parameters with sections of the the output. Use Table (instead of a dimension name) to set formatting characteristics for the entire table, Row for row specific formatting, Cell for cell specific, HdrRow for heading row specific, HdrCell for heading cell specific, and TopOfPage for title specific formatting.
The supported Style options are given below. See the Color dimension for more information on allowed colors.
Table 15 - Options within SSDim() Format Argument
| Bold |
Text is bolded. |
| Center |
Centered |
| CSpan |
Text is centered across several consecutive cells.
The text MUST be prefaced with '{n}'
where n denotes the number of cells. |
| Fill |
The text fills the cell. |
| Fit |
The text is sized to fit the cell. |
| Indent1 |
Indent the value 2em. |
| Indent2 |
Indent the value 4em. |
| Indent3 |
Indent the value 6em. |
| Italic |
Text is italicized. |
| Left |
Left Justified |
| LSpan |
Similar to CSpan except that the text is left justified. |
| NoBreak |
| Right |
Right Justified |
| RSPan |
Similar to CSpan except that the text is right justified. |
| Strike |
Text is show with a horizontal strike-thru. |
| UnderLine |
Text is underlined. |
| VBottom |
Align text on the bottom of the cell. |
| VCenter |
Vertically center the text in the cell. |
| VTop |
Align text to the top of the cell. |
| Wrap |
Text is wrapped if necessary to fit the cell. |
Examples
| |
SSDim(Dim:Neg Format::"#,###.00" TextColor::Red) |
Specifies formatting and color for points on Dim:Neg |
| |
SSDim(Dim:Neg Mask::1234) |
Alpha:"1,234.00" - same as Format(1234 Mask::SSDim(Dim:Neg Mask?)) |
| |
SSDim(Dim:Cus URL::"javascript:DrillDownToCus('*');") |
the DrillDownToCus function assumed to be defined (EchoS(Include::"xxx")) |
| |
SSDim(Dim:Alpha TextColor::Red FontSize::"80%" Style::"Bold,Underline,Italic") |
sets formats for Dim:Alpha |
| |
SSDim(Dim:Alpha CSS?) |
Alpha:"color: #ff0000; font-size: '80%';font-weight: bold; font-style: italic; text-decoration: underline;" |
Complex color (or style) schemes may become awkward when explicit dimensions must be declared and setup for each possible color/style/format combination. The next example shows how to achieve this by letting V4 automatically create dimensions for each combination. The example defines cell colors for each of the three rows output. Dates are formatted with a strike-thru if after 1-Jan-01. Text containing HOHOHO has a yellow cell color otherwise it has a light gray cell, brown text and is in italics.
Example 43 - Automatic Generation of Color/Format/Style Dimensions
| |
Dim CClr, TClr, TSty Dict /* CellColor, TextColor, TextStyle */
Dim SMask Shell
[SSD UV4:IsctFail]
Do(Context(BindEE(MakeI(SSD `MakeLC(DefQ(CClr*) CClr* DefQ(TClr*) TClr* DefQ(TSty*) TSty*)) MakeP(Dim:Dim Dim:SMask)))
SSDim(Dim* `MakeLC(DefQ(CClr*) CellColor::CClr* DefQ(TClr*) TextColor::TClr* DefQ(TSty*) Style::TSty*))
Dim*
)
[TDate UDate..] If({UDate* > UDate:010101} Then::[SSD TSty:Strike] Else::[SSD]):=UDate*
[TAlpha Alpha..]
If(Str(Alpha* UC? Has::"HOHOHO") Then::[SSD TClr:Yellow] Else::[SSD TClr:Brown TSty:Italic CClr:LightGray]):=Alpha*
[TestReport]
Do(Enum(Int:1..3
(Context(TEQ(int* 1 CClr:Red 2 CClr:White 3 CClr:Green))
EchoS([SSD]:=23123 [TDate UDate:010101] [TDate UDate:020101] [TAlpha "Now is the time"] [TAlpha "A HOHOHO to you"])
)))
|
The example below creates an HTML screen with 3 separate divisions or an Excel workbook with 3 sheets.
Example 44 - Multi-Sheet/Table Formatting
| |
[MultiSheetExample]
Do(SSDim(Table CSS::"empty-cells: show; border-collapse: collapse; background: transparent ; font-family: Arial; font-size: smaller ; border: 1px solid darkgrey;")
SSDim(Cell CSS::"border: 1px solid darkgrey; padding: 2px;")
SSDim(HdrRow CSS::"font-style: italic; background: pink;")
SSDim(TopOfPage CSS::"border: none;")
SSDim(Dim:Num Class::foo)
EchoS(CSS::".foo { color: blue; decoration: underline; }")
EchoS(Position::(Height::300 Width::150 Left::50 Top::150))
EchoS("Integer" "Square")
Enum(Int:1..20 @EchoS(Int* Num:={Int* * Int*}))
EchoS(End::"Table of Squares")
EchoS(CSS::".foo { color: blue; decoration: underline; }")
EchoS(Position::(Height::300 Width::150 Left::250 Top::150))
EchoS("Integer" "Cube")
Enum(Int:1..20 @EchoS(Int* Num:={Int* * Int* * Int*}))
EchoS(End::"Table of Cubes")
EchoS(CSS::".foo { color: blue; decoration: underline; }")
EchoS(Position::(Height::300 Width::150 Left::450 Top::150))
SSDim(Dim:Num Class::foo Format::"#.0000")
EchoS("Integer" "Root")
Enum(Int:1..20 @EchoS(Int* Sqrt(Int*)))
EchoS(End::"Math Tables of Interest")
)
|
StatAdjCosSim - Calculated Adjusted Cosine Similarity Function
Usage
| |
value = StatAdjCosSim ( xlist ylist zlist ) |
Parameters
| |
xlist |
The x or first argument list of numbers to be evaluated. |
| |
ylist |
The y or second argument list of numbers to be evaluated. |
| |
zlist |
The z or third argument list of numbers to be evaluated. If three lists are not specified then the four tagged values below must be given. |
Tagged Arguments
| |
Enum::lpt |
A list of points to be enumerated. |
| |
X::isct |
An intersection to be evaluated for each lpt. The result of the evaluations form the X or first argument list. |
| |
Y::isct |
An intersection to be evaluated for each lpt. The result of the evaluations form the Y or second argument list. |
| |
Z::isct |
An intersection to be evaluated for each lpt. The result of the evaluations form the Z or third argument list. |
Description
This module returns the adjusted cosine similarity between two vectors as described here.
StatAvg - Calculates Average
Usage
| |
value = StatAvg ( arg1 arg2 ... argn ) |
| |
value = StatAvg ( list ) |
| |
value = StatAvg ( tagarg ) |
Parameters
| |
value |
The arithmetic average of the elements in list. |
| |
argn |
A number |
| |
list |
The argument list of numbers to be evaluated. If no list is given then both Enum and Values tags must be specified. |
Tagged Arguments
| |
Enum::lpt |
A list of points to be enumerated. |
| |
Values::isct |
An intersection to be evaluated for each lpt. The result of the evaluations form the argument list. |
Tagged Results
| |
Distribution? |
If this argument is specified then the elements in the list describe not the sample points but the resulting distribution curve. This curve is converted to its corresponding sample points. Note that negative values are not allowed. Non-integer values are rounded to the nearest integer value. |
Description
StatAvg returns the average or arithmetic mean of its arguments- 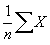
Examples
| |
StatAvg(Enum::Int:1..10 Values::Plus(Int* 25)) |
results in 30.5 |
| |
StatAvg(1 2 3 4 5) |
results in 3 |
| |
StatAvg((1 2 3 4 5)) |
also results in 3 |
| |
StatAvg(Enum::Employee.. Values::Employee.Salary) |
the average employee salary |
StatAvgDev - Average Deviation
Usage
| |
value = StatAvgDev ( list ) |
Parameters
| |
value |
The average deviation of the elements in list. |
| |
list |
The argument list of numbers to be evaluated. If no list is given then both Enum and Values tags must be specified. |
Tagged Arguments
| |
Enum::lpt |
A list of points to be enumerated. |
| |
Values::isct |
An intersection to be evaluated for each lpt. The result of the evaluations form the argument list. |
Tagged Results
| |
Distribution? |
If this argument is specified then the elements in the list describe not the sample points but the resulting distribution curve. This curve is converted to its corresponding sample points. Note that negative values are not allowed. Non-integer values are rounded to the nearest integer value. |
Description
This module returns the average of the absolute deviations of the points in list from their mean. The equation for calculating the average deviation is 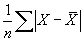
Examples
| |
StatAvgDev( (10 9 1 3 5) ) |
3.12 |
StatChiTest - Chi Squared Test for Independence
Usage
| |
value = StatChiTest ( constraints actlist expectedlist ) |
Parameters
| |
value |
to be documented. |
| |
constraints |
The number of degrees of freedom. |
| |
actlist |
A list of points corresponding to observed data. |
| |
expectedlist |
A list of points containing ratio of the totals to the grand total. |
Description
This module calculates the test for independence. The formula is show below-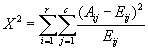
Examples
StatConfidence - Confidence Interval for a Population
Usage
| |
value = StatConfidence ( alpha stddev size ) |
Parameters
| |
alpha |
Significance level used to compute confidence level. |
| |
stddev |
The population standard deviation. |
| |
size |
The sample size. |
Description
This module returns the confidence interval for a population mean. This interval is a range on both sides of the mean so to get the actual range of values one must calculate the range as 
Examples
Assume that alpha is 0.05 (or that the confidence level is 100(1-alpha)% which is 95%) then we need to calculate the area under the standard normal curve (stddev = 1.0) that equals 95% which is +/- 1.96. The confidence interval is therefore 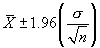 . If our sample is 100 apples with an average weight of 100 grams and a standard deviation of 1.8 then we can be 95% confident that the population mean is in the interval of
. If our sample is 100 apples with an average weight of 100 grams and a standard deviation of 1.8 then we can be 95% confident that the population mean is in the interval of 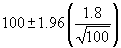 .
.
StatCorrel - Calculates Correlation between Two Lists
Usage
| |
value = StatCorrel ( xlist ylist ) |
Parameters
| |
xlist |
The x or first argument list of numbers to be evaluated. |
| |
ylist |
The y or second argument list of numbers to be evaluated. If two lists are not specified then the three tagged values below must be given. |
Tagged Arguments
| |
Enum::lpt |
A list of points to be enumerated. |
| |
X::isct |
An intersection to be evaluated for each lpt. The result of the evaluations form the X or first argument list. |
| |
Y::isct |
An intersection to be evaluated for each lpt. The result of the evaluations form the Y or second argument list. |
Description
This module returns the correlation coefficient of the members of the two lists. The formula is based on the StatCovar function and is 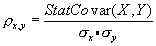
Examples
| |
StatCorrel((2 4 6 8 10) (1 2 3 4 5)) |
Num:1 |
| |
StatCorrel((2 4 5 8 10) (1 2 3 4 5)) |
Num:0.990148 |
StatCovar - Calculates Covariance between Two Lists
Usage
| |
value = StatCovar ( xlist ylist ) |
Parameters
| |
xlist |
The x or first argument list of numbers to be evaluated. |
| |
ylist |
The y or second argument list of numbers to be evaluated. If two lists are not specified then the three tagged values below must be given. |
Tagged Arguments
| |
Enum::lpt |
A list of points to be enumerated. |
| |
X::isct |
An intersection to be evaluated for each lpt. The result of the evaluations form the X or first argument list. |
| |
Y::isct |
An intersection to be evaluated for each lpt. The result of the evaluations form the Y or second argument list. |
Description
This module returns the covariance, or average of the products of deviations for each pair of points in the two lists. The formula is 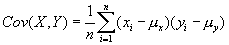
Examples
| |
StatCovar((2 4 6 8 10) (1 2 3 4 5)) |
Num:4 |
| |
StatCovar((10 9 8 7 6) (1 2 3 4 5)) |
Num:-2 |
StatCritBinom - Binomial Distribution Value is Less/Equal Criterion
Usage
| |
value = StatCritBinom ( trials probs alpha ) |
Parameters
| |
value |
The value k. |
| |
trials |
The number of Bernoulli trials. |
| |
probs |
The probability of a success on each trial. |
| |
alpha |
The criterion value. |
Description
The StatCritBinom module calculates the smallest integer, k, for which the cumulative binomial distribution function is greater than or equal to alpha.
Examples
| |
StatCritBinom(8 .3 .55) |
Num:2 |
StatDevSq - Calculates Square of Deviation from Average
Usage
| |
value = StatDevSq ( arg1 arg2 ... argn ) |
| |
value = StatDevSq ( list ) |
| |
value = StatDevSq ( tagarg ) |
Parameters
| |
value |
The sum of the squares of the deviations from the average. |
| |
argn |
A number |
| |
list |
The argument list of numbers to be evaluated. If no list is given then both Enum and Values tags must be specified. |
Tagged Arguments
| |
Enum::lpt |
A list of points to be enumerated. |
| |
Values::isct |
An intersection to be evaluated for each lpt. The result of the evaluations form the argument list. |
Description
StatDevSq returns the sum of the squares of the deviation from the average arguments- 
Examples
| |
StatDevSq((1 2 3 4 5 6)) |
results in 17.5 |
StatDist - Calculates a Point or Area of a Distribution
Usage
| |
value = StatDist ( restag arg arg ... ) |
Parameters
| |
value |
The result of the calculation, a point on the curve or cumulative area under the curve. |
| |
restag |
What type of distribution to calculate - see Result Tag below |
| |
arg |
One or more arguments depending on the type of distribution. |
Tagged Arguments
| |
A::npt |
An optional lower bounds for the Beta distribution, default is 0. |
| |
Alpha::npt |
The Alpha parameter to the distribution. |
| |
B::npt |
An optional upper bounds for the Beta distribution, default is 1. |
| |
Beta::npt |
The Beta parameter to the distribution. |
| |
Cumulative::npt |
True for the cumulative distribution (area under the curve), False for the point on the curve. |
| |
DoF::npt |
Degrees of freedom. This may be given more than once (example, the F distribution requires two degrees-of-freedom arguments). |
| |
Lambda::npt |
The lambda parameter to the distribution. |
| |
Mean::npt |
The mean. |
| |
Num::npt |
The number in the sample. |
| |
NumF::npt |
The number of failures. |
| |
NumP::npt |
The number in the population. |
| |
NumS::npt |
The number of successes. |
| |
ProbS::npt |
The probability of a success. |
| |
Samples::npt |
The number of samples. |
| |
StdDev::npt |
The standard deviation. |
| |
Trials::npt |
The number of trials. |
| |
X::npt |
The x argument to the distribution. |
| |
Z::npt |
The z argument to the distribution. |
Tagged Results
| |
BetaPDF? |
The cumulative beta probability density function. Required tags are X, Alpha, and Beta. Note that the X value must be in the range 0 <= x <= 1. If the X value is not in this range then the A and B parameters must be given to normalize the X value. |
| |
Binomial? |
The Individual term binomial distribution. Required tags are NumS, Trials, and ProbS. The Cumulative tag is optional and defaults to True. |
| |
ChiSq? |
The one-tailed probability of the chi-squared distribution. Required tags are X and DoF. |
| |
Exponential? |
The exponential distribution. The required tags are X and Lambda. The Cumulative tag is optional and defaults to True. |
| |
F? |
The F probability distribution. Required tags are X and DoF (two required). |
| |
Gamma? |
The gamma distribution. The required tags are X, Alpha, and Beta. The Cumulative tag is optional and defaults to True. |
| |
HyperGeo? |
The hypergeometric distribution. The required tags are Samples for number of successes in sample, Trials for number of trials, NumS for number in successes overall, and NumP is population size. |
| |
LogNorm? |
The lognormal distribution. The required tags are X, Mean, and StdDev. |
| |
NegBinom? |
The negative binomial distribution. Required tags are NumF, NumS, and ProbS. |
| |
Normal? |
The normal cumulative distribution. The required tags are X, Mean, and StdDev. The Cumulative tag is optional and defaults to True. |
| |
NormalStd? |
The standard normal cumulative distribution. The required tag is Z. |
| |
Poisson? |
The Poisson probability distribution. The required tags are X and Mean. The Cumulative tag is optional and defaults to True. |
| |
StudentT? |
The Student t-distribution. The required tags are X, DoF, and Tail. |
| |
Weibull? |
The Weibull distribution. The required tags are X, Alpha, and Beta. The Cumulative tag is optional and defaults to True. |
Description
BetaPDF Distribution
The cumulative beta distribution is based on four parameters- x the value at which to evaluate over the interval A..B, Alpha & Beta which are parameters to the distribution and A & B which are the lower & upper bounds of the function. The equation for the cumulative beta distribution, or incomplete beta function is- 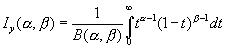 where y is
where y is 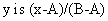
Binomial Distribution
The individual term binomial distribution probability. The arguments are NumS (the number of successes), Trials (the number of independent trials), ProbS (the probability of success per trial). The function can be calculated at a point or cumulatively. The formula for the probability mass function is 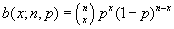 and the cumulative distribution function is
and the cumulative distribution function is 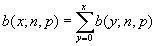
Chi-Square
Chi-Square returns the one-tailed probability of the chi-squared distribution. The arguments are (the value at which to calculate the function) and DoF (the degrees of freedom).
Exponential Distribution
This returns the exponential distribution function which is used to model the time between events. The arguments are X (the value of the function), Lambda (a parameter) and Cumulative (true for the cumulative, false for the density function). The formula for the density function is 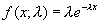 and the formula for the cumulative function is
and the formula for the cumulative function is 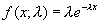
F Distribution
The F distribution is used to determine whether or not two data lists have different degrees of diversity. The arguments are X (the value at which to evaluate), DoF1 and DoF2 which are the numerator and denominator degrees of freedom. The equation is 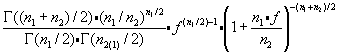 where n1 and n2 are the degrees of freedom.
where n1 and n2 are the degrees of freedom.
Gamma Distribution
The Gamma distribution function is used to study variables with a skewed distribution such as those found in queuing problems. The arguments are X (the value at which to evaluate), Alpha & Beta (parameters to the distribution), and Cumulative. When Alpha is a positive integer, this distribution is also known as the Erlang distribution which is commonly used in the telephone industry. The equation for the distribution is 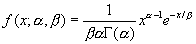
HyperGeometric Distribution
The hypergeometric function returns the probability of a given number of sample successes, NumS, given the sample size, Sample, population success PopS and population size NumP. The formula is given below where x is the NumS, n = Num, M is NumP and N = NumP.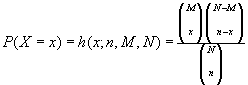
LogNormal
This returns the lognormal cumulative distribution. It is to be used when data has been logarithmically transformed. The formula is- 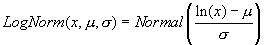
Negative Binomial Distribution
This distribution returns the probability of NumF failures before the NumS'th success when the probability of success is a constant ProbS. The formula is shown below where x corresponds to NumF, r is NumS and p is ProbS.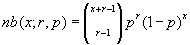
Normal Distribution
The normal distribution is calculated based on the formula below. The arguments are x, the value at which to calculate the distribution, the mean of the distribution, and the standard deviation.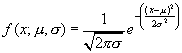
Normal Standard Distribution
The normal standard distribution returns the standard normal cumulative distribution with a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1. The formula is 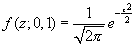
Poisson
The Poisson probability mass function is given by 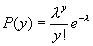 where lambda is the mean. The cumulative density function is given as
where lambda is the mean. The cumulative density function is given as 
Student's T
The Student's t-distribution which is used in the hypothesis testing of small sample lists. The formula for calculating is with the incomplete beta function- 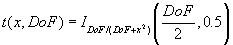
Weibull Distribution
The Weibull distribution is used for reliability analysis such as calculating the mean time to failure. The parameters to the function are x, the value at which to evaluate the function, alpha and beta which are parameters to the distribution. The equation for this distribution is 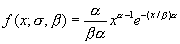
A note on calculating factorials
Several of the above distributions require the determination of factorials. The factorial grows very quickly and can overflow double precision floating point. V4 works with the log of the factorial instead of the actual value. When determining factorials for numbers above 1000, the Stirling approximation is used.
Examples
StatDistInv - The Inverse of a Distribution Function
Usage
| |
result = StatDistInv ( tagval prob arg ... ) |
Parameters
| |
result |
The inverse of the distribution specified by tagval. |
| |
prob |
The probability to find the inverse for. Always represented by the tagged value of Prob::npt. |
| |
arg |
One or more tagged argument as required by the distribution. |
Tagged Arguments
| |
A::npt |
An optional lower bounds for the Beta distribution, default is 0. |
| |
Alpha::npt |
The alpha parameter to the distribution. |
| |
B::npt |
An optional upper bounds for the Beta distribution, default is 1. |
| |
Beta::npt |
The beta parameter to the distribution. |
| |
DoF::npt |
Degrees of freedom. This may be given more than once (example, the F distribution requires two degrees-of-freedom arguments). |
| |
Mean::npt |
The mean. |
| |
Prob::npt |
The probability- the value at which to calculate the inverse. |
| |
StdDev::npt |
The standard deviation. |
Tagged Results
| |
BetaPDF? |
The cumulative beta probability density function. Required tags are Prob, Alpha, and Beta. |
| |
ChiSq? |
The one-tailed probability of the chi-squared distribution. Required tags are Prob and DoF. |
| |
F? |
The F probability distribution. Required tags are Prob and DoF (two required). |
| |
Gamma? |
The gamma distribution. The required tags are Prob, Alpha, and Beta. |
| |
LogNorm? |
The lognormal distribution. The required tags are Prob, Mean, and StdDev. |
| |
Normal? |
The normal cumulative distribution. The required tags are Prob, Mean, and StdDev. |
| |
NormalStd? |
The standard normal cumulative distribution. The required tag is Prob. |
| |
StudentT? |
The Student's t-distribution. The required tags are Prob, DoF, and Tail. |
Description
Examples
StatFisher - Calculates the Fisher Transformation
Usage
Parameters
| |
tran |
The Fisher transformation at point x. |
| |
x |
The point at which to calculate the transform. |
Description
This module returns the Fisher transformation at x. The formula is 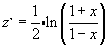
Examples
| |
StatFisher(.379949) |
Num:0.4 |
| |
StatFisher(.291313) |
Num:0.3 |
StatFisherInv - Inverse of the Fisher Transformation
Usage
| |
value = StatFisherInv ( y ) |
Parameters
| |
x |
The argument to the StatFisher transformation that would yield y. |
| |
y |
The point to find the inverse of. |
Description
This module returns the inverse of the Fisher transformation. The formula is 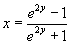
Examples
| |
StatFisherInv(.3) |
Num:0.291313 |
| |
StatFisherInv(.4) |
Num:0.379949 |
StatForecast - Forecast Value via Linear Trend
Usage
| |
yvalue = StatForecast ( x xlist ylist ) |
Parameters
| |
yvalue |
The forecasted y value |
| |
x |
The value at which to forecast |
| |
xlist |
A list of actual or known x values |
| |
ylist |
A list of actual or known y values |
Description
The StatForeCast module calculates the predicted yvalue for a given x and list of existing x and y values.
Examples
| |
StatForecast(6 (1 2 3 4 5) (2 4 6 8 10)) |
Num:12 |
StatFTest - Performs the F Test on Two Lists
Usage
| |
value = StatFTest ( xlist ylist ) |
Parameters
| |
value |
The result of the F test. |
| |
xlist |
The X or first argument list of numbers to be evaluated. |
| |
ylist |
The Y or second argument list of numbers to be evaluated. If two lists are not specified then the three tagged values below must be given. |
Tagged Arguments
| |
Enum::lpt |
A list of points to be enumerated. |
| |
X::isct |
An intersection to be evaluated for each lpt. The result of the evaluations form the X or first argument list. |
| |
Y::isct |
An intersection to be evaluated for each lpt. The result of the evaluations form the Y or second argument list. |
Description
This modules returns the result of an F-test which is the one-tailed probability that the variances in xlist and ylist are not significantly different.
Examples
| |
StatFTest( (1 2 3 4 5) (2 3 4 10 6) ) |
Num:0.208 |
StatGammaLn - Natural Log of the Gamma Function
Usage
| |
value = StatGammaLn ( list ) |
Parameters
Description
The module returns the natural logarithm of the gamma function
Examples
| |
StatGammaLn(4) |
Num:1.7918 |
StatGeoMean - Geometric Mean
Usage
| |
value = StatGeoMean ( list ) |
Parameters
| |
result |
The geometric mean of the elements in list. |
| |
list |
The argument list of numbers to be evaluated. If no list is given then both Enum and Values tags must be specified. |
Tagged Arguments
| |
Enum::lpt |
A list of points to be enumerated. |
| |
Values::isct |
An intersection to be evaluated for each lpt. The result of the evaluations form the argument list. |
Tagged Results
| |
Distribution? |
If this argument is specified then the elements in the list describe not the sample points but the resulting distribution curve. This curve is converted to its corresponding sample points. Note that negative values are not allowed. Non-integer values are rounded to the nearest integer value. |
Description
This module returns the geometric mean, as shown by the equation below, of its argument list.
Examples
| |
StatGeoMean((10 10)) |
Num:10 |
| |
StatGeoMean((1 2 3 4 5)) |
Num:2.60517 |
StatHarMean - Harmonic Mean
Usage
| |
value = StatHarMean ( list ) |
Parameters
| |
value |
The harmonic mean of the argument list. |
| |
list |
The argument list of numbers to be evaluated. If no list is given then both Enum and Values tags must be specified. |
Tagged Arguments
| |
Enum::lpt |
A list of points to be enumerated. |
| |
Values::isct |
An intersection to be evaluated for each lpt. The result of the evaluations form the argument list. |
Tagged Results
| |
Distribution? |
If this argument is specified then the elements in the list describe not the sample points but the resulting distribution curve. This curve is converted to its corresponding sample points. Note that negative values are not allowed. Non-integer values are rounded to the nearest integer value. |
Description
This module calculates the harmonic mean of its argument list. The harmonic mean is the reciprocal of the arithmetic mean of reciprocals as show by the equation 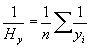
Examples
| |
StatHarMean((10 10)) |
Num:10 |
| |
StatHarMean((1 2 3 4 5)) |
Num:2.18978 |
StatKurtosis - Calculates Kurtosis of a List
Usage
| |
value = StatKurtosis ( list ) |
Parameters
| |
list |
The argument list of numbers to be evaluated. If no list is given then both Enum and Values tags must be specified. |
Tagged Arguments
| |
Enum::lpt |
A list of points to be enumerated. |
| |
Values::isct |
An intersection to be evaluated for each lpt. The result of the evaluations form the argument list. |
Tagged Results
| |
Distribution? |
If this argument is specified then the elements in the list describe not the sample points but the resulting distribution curve. This curve is converted to its corresponding sample points. Note that negative values are not allowed. Non-integer values are rounded to the nearest integer value. |
Description
This module returns the kurtosis, or relative sharpness/flatness of a data set defined by list. A positive number reflects a sharper peak while a negative number indicates a flatter curve. The formula is: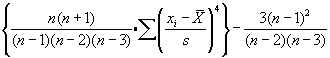
Examples
| |
StatKurtosis((10 11 10.4 12 9.8 11.8)) |
Num:-2.04855 |
| |
StatKurtosis((10 10 10.4 10 9.8 11.8)) |
Num:4.54674 |
StatLinFit - Fits a Line to a Set of Points
Usage
| |
value = StatLinFit ( tagarg ... ) |
Parameters
| |
value |
The result of the fit. The specific result depends on the arguments given. Note also that ancillary results may be returned as context points. |
| |
tagarg |
Tagged arguments described below. |
Tagged Arguments
| |
AbsDev::dim |
If given, then the calculated absolute deviation of the fit will be returned as a context point on this dimension. |
| |
At::list/pt |
A list or single point. After the best fit line has been determined, each of the points specified by this argument is taken as an x value and the corresponding y value is determined. |
| |
Bind::isct |
If specified then a binding is created with isct as the basis for each At point. Each At point is appended into the Bind intersection and the result is bound to the calculated y value of the fitted line. |
| |
ChiSq::dim |
If given, then the calculated chi-square of the fit will be returned as a context point on this dimension. |
| |
Context::dim |
If specified then each calculated y point (see At) is placed into the current context under this dimension. |
| |
Do::isct |
This option is used with the At parameter. The Do isct is evaluated for each calculated point determined by the fitted line and the At points. |
| |
Enum::list |
A list of points to enumerate through for x and y values. See X and Y below. |
| |
Intercept::isct |
If specified then the Y intercept of the fitted line is returned as a context point on this dimension. |
| |
Method::mode |
How the best fit is to be performed. Use SLLS for least squares fitting (default) or SLLAD for least absolute deviation. |
| |
Next::num |
Not yet implemented. |
| |
Slope::dim |
If specified then the slope of the fitted line is returned as a context point on this dimension. |
| |
StdDev::dim |
If given, then the calculated standard deviation of the fit will be returned as a context point on this dimension. |
| |
X::isct |
The intersection is evaluated for each point in the Enum list. The result is taken as the x value (see Y below). |
| |
Y::isct |
The intersection is evaluated for each point in the Enum list. The result is taken as the x value (see X above). |
Description
StatLinFit is a multi-purpose module for fitting a straight line to a series of points
Example 45 - StatLinFit Examples
| |
| Bind [FcstFGSales] |
|
| Enum(IM.. If::IM.IsFG |
|
| @StatLinFit(Enum::UMonth:9401..9612 Y::[Units],0 X::UMonth* Method::SLLAD |
|
|
At::UMonth* Context::Dim:Qty Do::[Explode]))" |
|
|
| Bind [Explode IM.. UMonth.. Qty..] |
|
| DEF(IM.BOM |
|
| Enum(IM.BOM @[Explode BOM.IM {BOM.Qty / IM.Yield * [FGFcst BOM.FGIM | Qty*],Qty*}]) |
|
| (Context(MakeP(Dim:Exp)) BindQ(Exp.IM IM*) BindQ(Exp.Qty Qty*) BindQ(Exp.UMonth UMonth*))) |
|
|
|
| Bind [SumByComCode] |
|
| Tally(Exp.. Context::Exp.IM |
|
| (Sum::{Exp.Qty * IM.StdCost * IM.CC.StdAdj,1.0} By::(IM.CC Exp.UMonth) Bind::[RMProj])) |
|
|
|
| Bind [RMProjection UMonth..] |
|
| Do([FcstFGSales] [SumByComCode] |
|
| MatrixS(Rows::CC.. RowCap::CC.Desc Columns::UMonth* ColCap::UMonth* Values::[RMProj],0)) |
|
|
|
| Bind [KidProj Cus..] |
|
| Int:=LT(StatLinFit(Enum::[PIList] X::List(Prior* Position::ProgId*) Y::[Kids],0 At::Plus(ListSize([PIList]) 1)) 0 0 Arg:1) |
|
|
StatMax - Returns Maximum Number in a List
Usage
| |
value = StatMax ( list cim ) |
Parameters
| |
list |
The argument list of numbers to be evaluated. If no list is given then both Enum and Values tags must be specified. |
| |
dim |
If specified, the result is returned on that dimension. |
Tagged Arguments
| |
Enum::lpt |
A list of points to be enumerated. |
| |
Values::isct |
An intersection to be evaluated for each lpt. The result of the evaluations form the argument list. |
Tagged Results
| |
Distribution? |
If this argument is specified then the elements in the list describe not the sample points but the resulting distribution curve. This curve is converted to its corresponding sample points. Note that negative values are not allowed. Non-integer values are rounded to the nearest integer value. |
Description
StatMin returns the largest number in the list. When the Enum and Values tags are used, the module returns the largest value. See the Optimize module to obtain the corresponding Enum value.
Examples
| |
StatMax((123 343 342 984 902)) |
984 |
StatMedian - Returns the Median Number of a List
Usage
| |
value = StatMedian ( list ) |
Parameters
| |
list |
The argument list of numbers to be evaluated. If no list is given then both Enum and Values tags must be specified. |
Tagged Arguments
| |
Enum::lpt |
A list of points to be enumerated. |
| |
Values::isct |
An intersection to be evaluated for each lpt. The result of the evaluations form the argument list. |
Tagged Results
| |
Distribution? |
If this argument is specified then the elements in the list describe not the sample points but the resulting distribution curve. This curve is converted to its corresponding sample points. Note that negative values are not allowed. Non-integer values are rounded to the nearest integer value. |
Description
This module returns the statistical median of a list of numbers. This is the number in the list such that there are an equal count of numbers in the list less than this number and greater than this number. By convention, if the list contains an even number of points then StatMedian returns the average of the two middle numbers.
Examples
| |
StatMedian( (1 2 3 4 5) ) |
3 |
| |
StatMedian( (1 2 3 4 5 6) ) |
3.5 (average of 3 & 4) |
| |
StatMedian( (1 2 3 10 11) ) |
3 |
| |
StatMedian( (1 2 3 10 11 12) ) |
6.5 |
StatMin - Returns the Minimum Number in a List
Usage
| |
value = StatMin ( list dim ) |
Parameters
| |
value |
The smallest number in the argument list. |
| |
list |
The argument list of numbers to be evaluated. If no list is given then both Enum and Values tags must be specified. |
| |
dim |
If specified, the result is returned on that dimension. |
Tagged Arguments
| |
Enum::lpt |
A list of points to be enumerated. |
| |
Values::isct |
An intersection to be evaluated for each lpt. The result of the evaluations form the argument list. |
Tagged Results
| |
Distribution? |
If this argument is specified then the elements in the list describe not the sample points but the resulting distribution curve. This curve is converted to its corresponding sample points. Note that negative values are not allowed. Non-integer values are rounded to the nearest integer value. |
Description
StatMin returns the smallest number in the list. When the Enum and Values tags are used, the module returns the smallest value. See the Optimize module to obtain the corresponding Enum value.
Examples
| |
StatMin((33 324 21 98)) |
21 |
| |
StatMin(Enum::Int:1..10 Values::Plus(Int* Int*)) |
2 |
StatMode - Calculates the Mode of a List
Usage
| |
value = StatMode ( list ) |
Parameters
| |
value |
The mode or most frequently occurring value in a list of numbers. |
| |
list |
The argument list of numbers to be evaluated. If no list is given then both Enum and Values tags must be specified. |
Tagged Arguments
| |
Enum::lpt |
A list of points to be enumerated. |
| |
Values::isct |
An intersection to be evaluated for each lpt. The result of the evaluations form the argument list. |
Tagged Results
| |
Distribution? |
If this argument is specified then the elements in the list describe not the sample points but the resulting distribution curve. This curve is converted to its corresponding sample points. Note that negative values are not allowed. Non-integer values are rounded to the nearest integer value. |
Description
This module returns the most frequently occurring value in a list of numbers. If there is no most frequently occurring number then the module fails.
Examples
| |
StatMode((1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 2 9 10)) |
Num:2 |
| |
StatMode((1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10)) |
fails - no most frequent value |
| |
StatMode((1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10)) |
-1 (returned because StatMode failed) |
StatPearson - Calculates Pearson Product Moment
Usage
| |
value = StatPearson ( xlist ylist ) |
Parameters
| |
xlist |
The x or first argument list of numbers to be evaluated. |
| |
ylist |
The y or second argument list of numbers to be evaluated. If two lists are not specified then the three tagged values below must be given. |
Tagged Arguments
| |
Enum::lpt |
A list of points to be enumerated. |
| |
X::isct |
An intersection to be evaluated for each lpt. The result of the evaluations form the X or first argument list. |
| |
Y::isct |
An intersection to be evaluated for each lpt. The result of the evaluations form the Y or second argument list. |
Description
This module returns the Pearson product moment correlation coefficient, r, which ranges from -1.0 to +1.0 as given by the formula below. It reflects the degree of a linear relationship between two lists.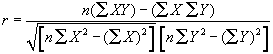
Examples
| |
StatPearson((1 2 3 4 5 6) (10 20 30 40 50 60)) |
Num:1 |
| |
StatPearson((6 5 4 3 2 1) (10 20 30 40 50 60)) |
Num:-1 |
| |
StatPearson((1 2 3 3 5 6) (10 20 30 40 50 60)) |
Num:0.976088 |
StatPercentile - Returns kth Percentile of List
Usage
| |
value = StatPercentile ( k list ) |
Parameters
| |
value |
The value from list (or interpolated) corresponding to the kth percentile. |
| |
k |
The percentile to select from list. |
| |
list |
A list of points. |
Description
This module returns the kthvalue point from the list.
Examples
| |
StatPercentile(0.3 (1 2 3 4)) |
returns 1.9 |
StatPermute - Number of Permutations for Given Number of Objects
Usage
| |
value = StatPermute ( number chosen ) |
Parameters
| |
value |
The number of permutations. |
| |
number |
The number of objects. |
| |
chosen |
The number chosen in each permutation. |
Description
This module returns the number of possible permutations of chosen objects out of a total of number objects. The equation for the calculation is 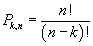
Examples
| |
StatPermute(100 3) |
Num:970200 |
| |
StatPermute(10 3) |
Num:720 |
| |
StatPermute(10 2) |
Num:90 |
StatProduct - Calculates the Product of a List
Usage
| |
value = StatProduct ( list ) |
Parameters
| |
list |
The argument list of numbers to be evaluated. If no list is given then both Enum and Values tags must be specified. |
Tagged Arguments
| |
Enum::lpt |
A list of points to be enumerated. |
| |
Values::isct |
An intersection to be evaluated for each lpt. The result of the evaluations form the argument list. |
Description
This module simply calculates the product of a list of numbers.
Examples
| |
StatProduct((1 2 3 4 5)) |
Num:120 |
StatQuartile - Returns a Quartile of a List
Usage
| |
value = StatQuartile ( k list ) |
Parameters
| |
value |
The value from list (or interpolated) corresponding to the kth quartile. |
| |
k |
The quartile (0, 1, 2, 3, or 4) to select from list. |
| |
list |
A list of points. |
Description
This module returns the kth quartile value point from the list. For k=0 this is the smallest point in the list, for k=4 it is the largest. For k=1, 2, and 3 it corresponds to calling StatPercentile with 0.25, .50, and .75 respectively.
Examples
| |
StatQuartile(2 (1 2 3 4)) |
returns 2.5 |
StatRan - Generates a Random Number
Usage
| |
value = StatRan ( tagarg ) |
Parameters
| |
value |
A random number. |
| |
tagarg |
One or more of the optional tagged arguments below. |
Tagged Arguments
| |
ListOf::num |
Generates a list of the integers from 1 to num in a random order. See the Offset argument to offset the numbers within the sequence. |
| |
Num::num |
Generate a random number between 1 and num. |
| |
Offset::value |
Use value as an additive offset to the integers return by the ListOf option. |
| |
Prob::list |
When this tag is specified, the result is not a random number but an integer index into an element of list. This list must be either a list of probabilities adding up to 1.0 OR a list of cumulative probabilities, the last element being 1.0. The returned index is determined by first generating a random number from 0 to 1 and then determining which list entry that number corresponds to. Internally, V4 maintains a list of cumulative probabilities from the list and then compares the generated random number to the list of cumulative probabilities, returning the index for the first cumulative value that is greater or equal to the random number. |
| |
Seed::num |
A starting seed value for the generator. Note that separate seeds are maintained for each of the generators. |
| |
Select::list |
Selects a random element from list. The list must contain at least one point. |
| |
To::num |
The generator creates a random number between 0 and 1. If this argument is given then an integer value between 0 and num will be returned. |
| |
Type::num |
The type of generator to use. 0 uses the standard generator that is part of the C runtime library and is not recommended. 1 uses a better algorithm and is the default. 2 is better than 1 but requires more CPU resources and is good for sequences of numbers into the low millions. Type 3 is the best generator (and most cpu expensive) and is good for sequence of virtually unlimited length (1018 numbers). |
Description
This module generates a pseudo-random sequence of numbers.
Examples
| |
StatRan() |
Num:7.82636925942561e-006 |
| |
StatRan(To::50) |
Int:7 |
| |
StatRan(ListOf::10) |
(Int:9 Int:5 Int:6 Int:10 Int:4 Int:3 Int:1 Int:2 Int:7 Int:8) |
| |
StatRan(ListOf::10 Offset::10) |
(Int:19 Int:15 Int:16 Int:20 Int:14 Int:13 Int:11 Int:12 Int:17 Int:18) |
| |
StatRan(Select::(now is the time)) |
now (for instance) |
StatRSQ - Calculates r2 Value of Two Lists
Usage
| |
value = StatRSQ ( ylist xlist ) |
Parameters
| |
value |
The r2 value of the linear regression line. |
| |
ylist |
The y or second argument list of numbers to be evaluated. If two lists are not specified then the three tagged values below must be given. |
| |
xlist |
The x or first argument list of numbers to be evaluated. |
Tagged Arguments
| |
Enum::lpt |
A list of points to be enumerated. |
| |
X::isct |
An intersection to be evaluated for each lpt. The result of the evaluations form the X or first argument list. |
| |
Y::isct |
An intersection to be evaluated for each lpt. The result of the evaluations form the Y or second argument list. |
Description
This value is the square of the Pearson product moment. This value can be interpreted as the proportion of the variance in y attributable to the variance in x 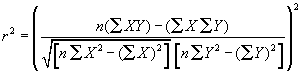
Examples
| |
StatRSQ((2 3 9 1 8 7 5) (6 5 11 7 5 4 4)) |
Num:0.0579502 |
| |
StatRSQ((2 3 9 2 8 7 5) (6 5 11 7 5 4 4)) |
Num:0.0786517 |
StatScale - Scales a List of Numbers
Usage
| |
reslist = StatScale ( list tagarg... ) |
Parameters
| |
reslist |
The resulting scaled list of numbers. |
| |
list |
A list of numbers to be scaled. |
| |
tagarg |
One or more tagged arguments below. |
Tagged Arguments
| |
Dim::dim |
The points of the resulting list, reslist, are to be points on this dimension. |
| |
Maximum::max |
Scale the points in the list such that the largest number becomes max. |
| |
Minimum::min |
Scale the points in the list such that the smallest number becomes min. |
| |
Offset::num |
Add num to each element of list. |
Description
This module performs various scaling operations on a list of numbers. All scaling is linear.
If both the Minimum and Maximum arguments are given then the points of the source list are scaled such that the smallest point becomes the Minimum value and the largest point becomes the Maximum value.
The dimension of the resulting list points are the same as those of the original list if all points in the original list are of the same dimension. If not then the resulting points are on Dim:Num. The use of the Dim tag overrides this logical and forces the resulting points to be of the specified dimension.
Examples
| |
StatScale((1 2 3 4 5) Minimum::50) |
(Int:50 Int:51 Int:52 Int:53 Int:54) |
| |
StatScale((1 2 3 4 5) Maximum::100) |
(Int:96 Int:97 Int:98 Int:99 Int:100) |
| |
StatScale((1 2 3 4 5) Maximum::100 Minimum::50) |
(Int:50 Int:63 Int:75 Int:88 Int:100) |
| |
StatScale((1 2 3.0 4 5) Maximum::100 Minimum::50) |
(Num:50 Num:62.5 Num:75 Num:87.5 Num:100) |
StatSkew - Calculates the Skew of a List
Usage
| |
value = StatSkew ( list ) |
Parameters
| |
list |
The argument list of numbers to be evaluated. If no list is given then both Enum and Values tags must be specified. |
Tagged Arguments
| |
Enum::lpt |
A list of points to be enumerated. |
| |
Values::isct |
An intersection to be evaluated for each lpt. The result of the evaluations form the argument list. |
Tagged Results
| |
Distribution? |
If this argument is specified then the elements in the list describe not the sample points but the resulting distribution curve. This curve is converted to its corresponding sample points. Note that negative values are not allowed. Non-integer values are rounded to the nearest integer value. |
Description
This module calculates the skewness of a distribution. Positive skewness indicates a distribution with its tail more towards positive values, negative with an asymmetric tail towards the negative. The formula for calculating skewness is 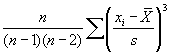
Examples
| |
StatSkew((1 2 3 4 5 6)) |
Num:0 |
| |
StatSkew((1 2 3 3 3 4 5 6)) |
Num:0.301953 |
| |
StatSkew((1 0 0 2 3 4 5 6)) |
Num:0.22625 |
| |
StatSkew((1 -1 -1 2 3 4 5 6)) |
Num:-0.0988396 |
StatSlope - Calculates Slope on Linear Regression of Two Lists
Usage
| |
slope = StatSlope ( xlist ylist ) |
Parameters
| |
slope |
The slope of the linear regression line through the points determined by xlist and ylist. |
| |
xlist |
The x or first argument list of numbers to be evaluated. |
| |
ylist |
The y or second argument list of numbers to be evaluated. If two lists are not specified then the three tagged values below must be given. |
Tagged Arguments
| |
Enum::lpt |
A list of points to be enumerated. |
| |
X::isct |
An intersection to be evaluated for each lpt. The result of the evaluations form the X or first argument list. |
| |
Y::isct |
An intersection to be evaluated for each lpt. The result of the evaluations form the Y or second argument list. |
Description
This module calculates the slope for the linear regression line through the point pairs specified by xlist and ylist. The formula for the calculation is 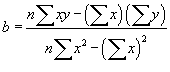
Examples
| |
StatSlope((3 6 9 12 15 18) (1 2 3 4 5 6)) |
Num:0.333333 |
StatStandardize - Returns a Normalized Value
Usage
| |
value = StatStandardize ( x mean stddev ) |
Parameters
| |
value |
The standardized value. |
| |
x |
The value at which to calculate. |
| |
mean |
The mean of the distribution. |
| |
stddev |
The standard deviation of the distribution. |
Tagged Arguments
| |
Enum::lpt |
A list of points to be enumerated. |
| |
Values::isct |
An intersection to be evaluated for each lpt. The result of the evaluations form the argument list. |
Description
This module returns a normalized value from a distribution given by its mean and standard deviation. The equation for calculating the standardization is 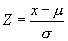
Examples
| |
StatStandardize(36 34 2.3) |
Num:0.869565 |
StatStdDev - Calculates the Standard Deviation of a Sample
Usage
| |
value = StatStdDev ( list ) |
Parameters
| |
list |
The argument list of numbers to be evaluated. If no list is given then both Enum and Values tags must be specified. |
Tagged Arguments
| |
Enum::lpt |
A list of points to be enumerated. |
| |
Values::isct |
An intersection to be evaluated for each lpt. The result of the evaluations form the argument list. |
Tagged Results
| |
Distribution? |
If this argument is specified then the elements in the list describe not the sample points but the resulting distribution curve. This curve is converted to its corresponding sample points. Note that negative values are not allowed. Non-integer values are rounded to the nearest integer value. |
Description
The StatStdDev module returns an estimate for the standard deviation based on a the sample list as show by the equation 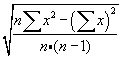
Examples
| |
StatStdDev((10 11 12 11 14 9 10)) |
Num:1.63299 |
| |
StatStdDev((9.8 9.9 10 9.8 10 9.9)) |
Num:0.0894427 |
StatStdDevP - Standard Deviation of a Population
Usage
| |
value = StatStdDevP ( list ) |
Parameters
| |
value |
The standard deviation. |
| |
list |
The argument list of numbers to be evaluated. If no list is given then both Enum and Values tags must be specified. |
Tagged Arguments
| |
Enum::lpt |
A list of points to be enumerated. |
| |
Values::isct |
An intersection to be evaluated for each lpt. The result of the evaluations form the argument list. |
Tagged Results
| |
Distribution? |
If this argument is specified then the elements in the list describe not the sample points but the resulting distribution curve. This curve is converted to its corresponding sample points. Note that negative values are not allowed. Non-integer values are rounded to the nearest integer value. |
Description
StatStdDevP calculates the standard deviation where list is the entire population. The formula is 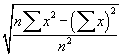
Examples
| |
StatStdDevP((10 11 12 11 14 9 10)) |
Num:1.51186 |
| |
StatStdDevP((9.8 9.9 10 9.8 10 9.9)) |
Num:0.0816497 |
StatStdErrYX - Standard Error of Regression
Usage
| |
value = StatStdErrYX ( ylist xlist ) |
Parameters
| |
value |
The standard error of regression for the list of x & y values. |
| |
ylist |
The y or second argument list of numbers to be evaluated. If two lists are not specified then the three tagged values below must be given. |
| |
xlist |
The x or first argument list of numbers to be evaluated. |
Tagged Arguments
| |
Enum::lpt |
A list of points to be enumerated. |
| |
X::isct |
An intersection to be evaluated for each lpt. The result of the evaluations form the X or first argument list. |
| |
Y::isct |
An intersection to be evaluated for each lpt. The result of the evaluations form the Y or second argument list. |
Description
This module calculates the standard error of the regression. The equation is: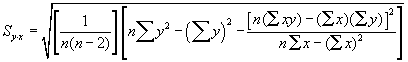
Examples
| |
StatStdErrYX((2 4 6 8 10) (1 2 3 4 5)) |
Num:0 |
| |
StatStdErrYX((2 4 5 9 10) (1 2 3 4 5)) |
Num:0.795822 |
StatSumSq - Calculates the Sum of Squares of a List
Usage
| |
value = StatSumSq ( list ) |
Parameters
| |
value |
The sum of the squares of the points in list. |
| |
list |
The argument list of numbers to be evaluated. If no list is given then both Enum and Values tags must be specified. |
Tagged Arguments
| |
Enum::lpt |
A list of points to be enumerated. |
| |
Values::isct |
An intersection to be evaluated for each lpt. The result of the evaluations form the argument list. |
Description
The module returns the sum of the squares of all the points in list as shown by the equation 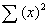
Examples
StatSumX2mY2 - Sum of X2 minus Y2
Usage
| |
value = StatSumX2mY2 ( xlist ylist ) |
Parameters
| |
value |
The sum of the differences of the squares. |
| |
xlist |
The x or first argument list of numbers to be evaluated. |
| |
ylist |
The y or second argument list of numbers to be evaluated. If two lists are not specified then the three tagged values below must be given. |
Tagged Arguments
| |
Enum::lpt |
A list of points to be enumerated. |
| |
X::isct |
An intersection to be evaluated for each lpt. The result of the evaluations form the X or first argument list. |
| |
Y::isct |
An intersection to be evaluated for each lpt. The result of the evaluations form the Y or second argument list. |
Description
StatX2mY2 returns the sum of the differences of the squares as shown by the equation 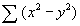
Examples
| |
StatSumX2mY2((1 2 3 4 5) (1 2 3 4 5)) |
Num:0 |
| |
StatSumX2mY2( (1 2 3 4 5) (10 9 8 7 6)) |
Num:-275 |
StatSumX2pY2 - Sum of X2 plus Y2
Usage
| |
value = StatSumX2pY2 ( xlist ylist ) |
Parameters
| |
value |
The sum of the sum of the squares. |
| |
xlist |
The x or first argument list of numbers to be evaluated. |
| |
ylist |
The y or second argument list of numbers to be evaluated. If two lists are not specified then the three tagged values below must be given. |
Tagged Arguments
| |
Enum::lpt |
A list of points to be enumerated. |
| |
X::isct |
An intersection to be evaluated for each lpt. The result of the evaluations form the X or first argument list. |
| |
Y::isct |
An intersection to be evaluated for each lpt. The result of the evaluations form the Y or second argument list. |
Description
This module returns the sum of the sum of the squares of the points in the two lists as shown by the equation 
Examples
| |
StatSumX2pY2((1 2 3 4 5) (1 2 3 4 5)) |
Num:110 |
| |
StatSumX2pY2((1 2 3 4 5) (10 9 8 7 6)) |
Num:385 |
StatSumXmY2 - Sum of X Minus Y2
Usage
| |
value = StatSumXmY2 ( xlist ylist ) |
Parameters
| |
value |
The sum of the differences of the squares. |
| |
xlist |
The x or first argument list of numbers to be evaluated. |
| |
ylist |
The y or second argument list of numbers to be evaluated. If two lists are not specified then the three tagged values below must be given. |
Tagged Arguments
| |
Enum::lpt |
A list of points to be enumerated. |
| |
X::isct |
An intersection to be evaluated for each lpt. The result of the evaluations form the X or first argument list. |
| |
Y::isct |
An intersection to be evaluated for each lpt. The result of the evaluations form the Y or second argument list. |
Description
The StatSumXmY2 module returns the sum of the differences between x and y squared. The equation is 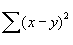
Examples
| |
StatSumXmY2((1 4 9 16) (1 2 3 4)) |
Num:184 |
StatTrimMean - Mean of Interior of List
Usage
| |
value = StatTrimMean ( percent list ) |
Parameters
| |
value |
The resulting mean. |
| |
percent |
The percentage to take from both sides of the list. Half are taken from the beginning of the list and half from the end. |
| |
list |
The argument list of numbers to be evaluated. If no list is given then both Enum and Values tags must be specified. |
Tagged Arguments
| |
Enum::lpt |
A list of points to be enumerated. |
| |
Values::isct |
An intersection to be evaluated for each lpt. The result of the evaluations form the argument list. |
Description
This module calculates the mean of a list of numbers. The original list is sorted in ascending order and half of the number to exclude are taken from the front and half from the end.
Examples
StatTTest - Probability Associated with a Student T Test
Usage
| |
value = StatTTest ( list1 list2 tails type ) |
Parameters
| |
list1 |
The first data set. |
| |
list2 |
The second data set. |
| |
tails |
1 for one-tailed distribution, 2 for two-tailed. |
| |
type |
1 for paired, 2 for equal variance (homoscedastic), 3 for unequal variance (heteroscedastic) |
Description
This module returns the probability associated with a Student's t-test. For equal variance, the equations are 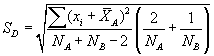 and
and 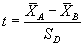 For unequal variance the following equation is used-
For unequal variance the following equation is used- 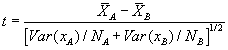 And for paired-
And for paired- 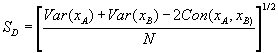 and
and 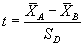
Examples
StatVar - Returns the Variance of a List
Usage
Parameters
| |
value |
The variance of the list. |
| |
list |
The argument list of numbers to be evaluated. If no list is given then both Enum and Values tags must be specified. |
Tagged Arguments
| |
Enum::lpt |
A list of points to be enumerated. |
| |
Values::isct |
An intersection to be evaluated for each lpt. The result of the evaluations form the argument list. |
Tagged Results
| |
Distribution? |
If this argument is specified then the elements in the list describe not the sample points but the resulting distribution curve. This curve is converted to its corresponding sample points. Note that negative values are not allowed. Non-integer values are rounded to the nearest integer value. |
Description
StatVar returns an estimate of the variance of a population given a sample in list. Note that if the data in list represents the entire population, StatVarP should be used. The formula for calculating StatVar is 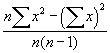
Examples
| |
StatVar((2 3 4 5 6 7)) |
Num:3.5 |
| |
StatVar((100 101 102.4 99)) |
Num:2.10667 |
StatVarP - Returns the Variance of a Population
Usage
| |
value = StatVarP ( list ) |
Parameters
| |
list |
The argument list of numbers to be evaluated. If no list is given then both Enum and Values tags must be specified. |
Tagged Arguments
| |
Enum::lpt |
A list of points to be enumerated. |
| |
Values::isct |
An intersection to be evaluated for each lpt. The result of the evaluations form the argument list. |
Tagged Results
| |
Distribution? |
If this argument is specified then the elements in the list describe not the sample points but the resulting distribution curve. This curve is converted to its corresponding sample points. Note that negative values are not allowed. Non-integer values are rounded to the nearest integer value. |
Description
StatVarP returns an estimate of the variance of a population assuming that list is the entire population. If list is only a sample then StatVar should be used. The equation is 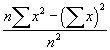
Examples
| |
StatVarP((2 3 4 5 6 7)) |
Num:2.91667 |
| |
StatVarP((100 101 102.4 99)) |
Num:1.58 |
StatZTest - Two Tailed P Value of a Z Test
Usage
| |
value = StatZTest ( x sigma list ) |
Parameters
| |
x |
The value to test. |
| |
sigma |
The population standard deviation |
| |
list |
The argument list of numbers to be evaluated. If no list is given then both Enum and Values tags must be specified. |
Tagged Arguments
| |
Enum::lpt |
A list of points to be enumerated. |
| |
Values::isct |
An intersection to be evaluated for each lpt. The result of the evaluations form the argument list. |
Description
This module returns the two-tailed P-value of a z-test. The formula is:
Examples
| |
StatZTest(5.3 2.0 ( 3 6 10 9 9 12)) |
Num:0.000223186 |
Str - Perform Various String Functions
Usage
| |
result = Str ( string tagarg ) |
| |
result = Str ( point point ... tagarg ) |
| |
value = nStr ( arguments same as Str ) |
Parameters
| |
result |
The result of the module - varies depending on the arguments. |
| |
string |
A string or dictionary entry point. |
| |
point |
Any V4 point |
| |
tagarg |
One or more tagged arguments as described below. |
Tagged Arguments
| |
After::str |
Returns the portion of the string found after the first (or last) occurrence of str. An error is generated if str is not found within the string. You may use the three-colon tag option to override the error and return the entire source string if str is not found. See also the Anchor option. |
| |
All::list |
Returns TRUE if all elements of the list are found within the string. This may be used with the IC or UC options. If any element is not found then FALSE is returned. |
| |
All::pattern |
Searches the string for all occurences of the regular expression pattern. The returned result is a list of Int2 points denoting the starting and ending positions of each found occurence. Any Str arguments after this tag are processed as List arguments. Note that regular expression may contain multiple patterns, each of which must be enclosed within parentheses. |
| |
All::class |
Returns TRUE if all characters in the string are elements of class, where class is one of: Alpha (alphabetic characters), Digit (one of the digits 0 through 9), Hex (a hexadecimal character), Id (a valid identifier character), Lowercase (a lower case character), Octal (an octal digit 0 through 7), Print (a printable character), Punctuation (a puncuation character), Uppercase (an uppercase character), Whitespace (a white space character, e.g. space, tab). |
| |
Anchor::pos |
Determines the anchor point for the Before, After, and Has search options. The default is Anchor:LHS which sets the search anchor on the left side (beginning) of the string. The other option is Anchor:RHS which sets the search anchor on the right side (end) of the string. The default is to search for the first occurance of a substring. When the anchor is set to the right hand side the search is for the last occurance of the substring. |
| |
Any::class |
Returns TRUE if any of the characters in the string are elements of class. See the All option for more details. |
| |
Before::str |
Returns the portion of the string found before the first (or last) occurrence of str. An error is generated if str is not found within the string. You may use the three-colon tag option to override the error and return the entire source string if str is not found. See also the Anchor option. |
| |
Begin::num |
References the beginning character of a substring. Positive numbers reference from the left (1 is first). Negative numbers reference from the right (-1 is last character). Used with End or Length. |
| |
Break::list |
Breaks the first argument string into a list of substrings based on the Integer or Int2 elements of the list. If the list consists of n integers then the string will be broken into n+1 substrings using then integers as byte offsets. The first character of the string is byte 1. If the list consists of n int2 points then a list of 2* n+1 substrings. |
| |
Break::chars |
Breaks the first argument string into a list of two substrings broken on one of the chars. If the next argument is Trim? then the breaking character is not included, otherwise it is included in the second string. If chars is the empty string then V4 breaks on space/tab/period/comma. If no breaking character is found within the first argument then the result is a list consisting of the first argument string and an empty string. |
| |
Break::int2 |
Breaks the first argument string into 3 pieces based on the two values within int2. The first piece is all characters up to the first value in int, the second is the characters denoted by the two values, and the third is all characters after the second value. |
| |
Count::class |
Returns the number of characters in the string which are elements of class. See the All option for more details. |
| |
Decode::Base64 |
Decodes the string previously encoded in the base 64 format. |
| |
Decode::DES |
Decodes the string using the Data Encryption Standard. A Key must be specified before this option is used. See also Key and Encode. |
| |
Decode::Hex |
Decodes sequences of 4 byte hexadecimal numbers to the corresponding UNICODE characters. |
| |
Decode::Hex8 |
Decodes sequences of 2 byte hexadecimal numbers to the corresponding UNICODE characters. |
| |
Decode::XML |
Decodes an valid XML string converting XML entities to characters. |
| |
Decode::XOR |
Decodes each 16 byte character by XOR'ing it with a previously specified key. A Key must be specified before this option is used. See also Key and Decode. |
| |
Decode::XOR8 |
Decodes each 8 byte character by XOR'ing with a key. A Key must be specified before this option is used. See also Key and Decode. |
| |
Empty::log |
Tests for an empty string and returns TRUE or FALSE. If the string is empty and log is TRUE then TRUE is returned. If the string is not empty and log is FALSE then TRUE is also returned. Otherwise FALSE is returned. A string is considered empty if it is zero-length, or contains nothing but white space and control characters. |
| |
Encode::Base64 |
Encodes the string in base 64 format. |
| |
Encode::DES |
Encodes the string using the Data Encryption Standard. A Key must be specified before this option is used. Note that the resulting string may be longer than the source string. See also Key and Decode. |
| |
Encode::Hex |
Encodes each 16 byte character as a sequece of 4 hexadecimal numbers. |
| |
Encode::Hex8 |
Encodes each 8 byte character as sequence of 2 hexadecimal numbers. |
| |
Encode::XML |
Encodes the string such that it is a valid XML string. Special characters (ampersand, less-than) are converted to XML entities. |
| |
Encode::XOR |
Encodes each 16 byte character by XOR it with a previously specified key. A Key must be specified before this option is used. See also Key and Decode. |
| |
Encode::XOR8 |
Encodes each 8 byte character by XOR'ing with a key. A Key must be specified before this option is used. See also Key and Decode. |
| |
End::num |
References the ending character of a substring. Positive numbers reference from the left (1 is first). Negative numbers reference from the right (-1 is last character). Used with Begin. |
| |
Escape::char |
Sets the string literal escape characters to char. |
| |
Escape::UV4:none |
No escape character is defined (see Literal tag below). |
| |
Escape::HTML |
Converts any embedded ending characters to the HTML entity format. |
| |
Evaluate::pattern |
This option scans through the first argument string looking for each instance of pattern. When found V4 then scans for the mirror image of pattern. The text between the first pattern and the mirror image is then evaluated as a V4 point. The resulting point is converted to a string and inserted within the source string. If the text between the pattern and its mirror represent a non-intersection point then an intersection is created containing just that point. The mirror image of pattern is determined by reversing the order of the characters in pattern and converting left parentheses, brackets braces, etc. to the right-handed equivalent. |
| |
Exact::list |
This option attempts to match string with one of the elements of list. The module returns an index to the first point in list that exactly matches the string or Logical:False if no match is detected. The UC? tag can be used for case-insensitive matches. |
| |
Exact::xstr |
Returns Int:1 if xstr exactly matches string. The UC? tag can be used for case-insensitive matches. Logical:False is returned if the two strings do not match. |
| |
Group::num |
Return the value of the numth regular expression group matched. |
| |
Has::list |
Search the first argument string for an occurrence of any of the elements within list. The module returns the first element index within list that was matched within the string. If no element matches then Logical:False is returned. If any element of the list is empty then it is ignored. If all elements of the list are empty then an error is thrown. |
| |
Has::str |
Search the first argument string for an occurrence of str. If it is found then the starting character in the first argument is returned. If the str is not found then Logical:No is returned. If str is empty then an error is thrown. See also the Anchor option. |
| |
Hash::mode |
Hashes the string based on the hash mode. The supported modes are: 32 to return a 32 bit (Dim:Int) hash value, 64 to return a 64 bit (Dim:Int2) hash value, CRC to return a 32 bit cyclic redundancy check code, MD5 to return the MD5 checksum. The result is returned as a 32-byte string. Note: there is the potential for ambiguity when calculating this value on V4 strings. If the string contains NO UNICODE characters (values greater than 255), then a calculation is performed on 8-bit characters even if the string is UNICODE. If any character values greater than 255 are in the string then the calculation is performed on 16-bit characters. SHA256 to return the SHA-256 hash of the first argument as a 64-byte hex string. SHA1 to return then SHA-1 hash of the first argument. The MD5, SHA256 and SHA1 hashes may be prefaced with a Key:key argument to perform HMAC-SHA256 / HMAC-SHA1 hashing. |
| |
Head::str |
Returns Int:1 if the first argument string begins with str or Logical:No if it does not begin with str. |
| |
Head::list |
Compares the beginning of the first argument string with each member of list. If a member of the list begins the string then the index of that member is returned, otherwise Logical:No is returned. |
| |
Head::num |
Returns the first num characters of the string. If num is negative then it refers to the end of the string (i.e. -1 is the entire string, -2 is the entire string minus the last character, -3 is minus the last 2 characters, etc.). If num is 0 (zero) then an empty string is returned. |
| |
HTML::ASCII |
Converts the string to a 7-bit HTML printable string. Any special or UNICODE characters are converted to the HTML ';#nnnn;' format. |
| |
Key::value |
Specifies the key to be used for Encode and Decode See also Encode and Decode. This may also be used for several of the hashing functions. |
| |
Length::num |
References the length of a substring. Used with Begin. See the Maximum option within the Format module to truncate a string to a maximum length. |
| |
ListOf::chars |
Converts the first argument into a list of substrings broken on any of the chars. If the next argument is Trim? then the break characters are NOT included. Any Str arguments after this tag are processed as List arguments. |
| |
ListOf::keyword |
Creates a list of strings based on the keyword value. If Keyword is TAB then the source string is considered tab-delimited text. If the keyword is CSV then the source string is parsed as comma-separated-values. If the keyword is INTEGER then a list of integers is returned corresponding to the ASCII/UNICODE value of the characters in the string is returned. If keyword is CHARACTERS then the argument string is broken into a list of characters (same as ListOf?). |
| |
Literal::char |
Converts the string to a literal enclosed by the character char. Any occurrences of char within the string are prefaced with the escape character (usually the backslash) or if no escape character is defined then the char is doubled. If the escape character is the backslash then all non-printable characters are converted to their octal equivalents. Any occurrences of the escape character are also doubled within the string. If char is a left character (left-paren, left-bracket, left-brace, etc.) then the ending character is automatically converted to the right version of the character. |
| |
Literal::HTML |
Converts the string to a valid javascript single-quoted string. |
| |
New::patstr |
Replace the source string with patstr. If a regular expression pattern has been matched on the source string then the patstr may include escape sequences referencing matched groups within the source string. The escape sequences are of the form '~1' '~2' ... '~9' which correspond to matched groups 1 through 9. The tilde escape character may be changed with the Escape argument. |
| |
None::class |
Returns TRUE if none of the characters in the string are elements of class. See the All option for more details. |
| |
Nth::num |
Returns the numth character from the source string. A range or list of numbers is also allowed. See example below. If any of the numbers are less than 1 or greater than the length of the source string then an error is generated. |
| |
Num::num |
Determines the number of Replace/With occurences, the default is 1. Use Num? to replace all occurences. Note that this tag must precede the With tag. |
| |
Partial::pstr |
Returns the number of initial characters string shares with pstr. If either string is 0-length or none of the initial characters match then Int:0 is returned. If only the first characters match then Int:1 is returned. If the first two characters match then Int:2, etc. |
| |
Random::length |
Returns a string of length characters randomly chosen from the source string. This option may be used to generate a random sequence of characters from an arbitrary set of characters. |
| |
RegExp::list |
The same as the Replace:list option except the pattern strings are treated as regular expressions, not literal strings. |
| |
RegExp::pattern |
Search for the regular expression pattern within the first argument. |
| |
Replace::str |
Search for the pattern str within the first argument. See the With argument. |
| |
Replace::num |
If a regular expression pattern has been matched then replace the numth group with the string specified by the With tag. |
| |
Replace::list |
A list may be given to perform multiple replacements within a single module call. The list is actually a list of lists. Each main list entry is a two part list. The first element being the string to match and the second being the replacement string. This form does not use the With or Num? tags. |
| |
Soundex::type |
Returns the SOUNDEX code for the current string. If option is ALPHA then a 4 character soundex value is returned. If option is NUMERIC then a 4-5 digit number is returns (where the first 1-2 digits are the numeric value (1-26) of the ALPHA value's first character. If option is MYSQL then a 4-? character string is returned corresponding to the mySQL SOUNDEX() function. |
| |
Split::substr |
This option splits a string into a list based on the substr pattern. V4 searches the source string for all occurances of substr and creates a list of the split string segments between the substr matches. Unlike the ListOf options, the substr is not included in the resulting list. |
| |
Start::num |
Identical to Begin:num. |
| |
Sub::key |
Performs a simple substitution cipher on the string based on the contents of key. The key can be up to 36 characters in length. The first 26 characters are the characters to be substituted for the letters 'A' through 'Z' - i.e. the first character in key replaces any instances of 'A' in the string, the second character any instances of 'B', etc. The 27th through 36th characters are used to replace the digits '0' through '9'. If key is less than 36 characters then only those characters in the string with a corresponding subsitution character will be replaced. Case is preserved in this operation. |
| |
Tail::str |
Returns Logical:True if the first argument string ends with str, Logical:False otherwise. |
| |
Tail::list |
Compares the end of the first argument string with each member of list. If a member of the list ends the string then the index of that member is returned, otherwise Logical:No is returned. |
| |
Tail::num |
Returns the last num characters of the string. If num is negative then it references the beginning of the string (i.e. -1 is the entire string, -2 is the entire string minus the first character, -3 is the string minus the first 2 characters, etc.). If num is 0 (zero) then an empty string is returned. |
| |
Trim::how |
Trims off leading and/or trailing white-space characters from the string. The argument, how, must be one of the following: All to trim leading and trailing characters (see also Trim?), Left to trim just the leading characters and Right to trim just trailing characters. |
| |
URL::option |
If option is ENCODE or UTF8 then encode the string according to URL specifications. If the option is DECODE then decode the URL string. UNICODE may also be specified in which case a character greater than FF16 are encoded as '%uxxxx where xxxx is the four-digit hexadecimal representation of the character. |
| |
Width::num |
Identical to Length:num. |
| |
With::num |
If a regular expression pattern has been matched then replace the Replace string with the numth group of the pattern. |
| |
With::newstr |
Replace the matched str via the Replace tag with newstr. |
| |
Word::str |
Tries to match str in the first argument string as a word meaning that str is delimited by punctuation or white space. The '*' character may be used for wild-card matching on either side of str. For example, Word::"go*" would match on the words "go", "going", "goes", "gone", etc. Word::"*ing" would match on any word ending with "ing". Word::"*xxx*" is identical to Has::"xxx". |
| |
XML::list |
See the Do module for a complete description of this feature. |
| |
XML::xmlstring |
Evaluates the remaining arguments normally and then encloses the results within the XML tag specified by xmlstring. Multiple XML tags may be specified within a single Str module. If the argument is UV4:none then it is ignored. |
Tagged Results
| |
Capitalize? |
Capitalizes the first letter of each word in the string, all other letters are set to lower case (same as Title?). |
| |
Empty? |
Returns TRUE if the string is empty or contains only white-space characters, FALSE otherwise. |
| |
Group? |
Return all regular expression groups matched as a list of strings. Any Str arguments after this tag are processed as List arguments. |
| |
HTML? |
Converts the string such that it will output properly as HTML. It converts all '&' characters to '&' and '<' characters to '<'. |
| |
IC? |
Ignore case on all subsequent string comparisons within the current Str module. |
| |
LC? |
Converts the string to lower case. |
| |
Length? |
Returns the current length of the string. See also Len. |
| |
ListOf? |
Converts the first argument string into a list of characters. See also Num(Listof?). |
| |
Literal? |
Same as Literal:"\"". |
| |
Num? |
Replace all occurences of the Replace string (with no error if no occurences). Note that this tag must precede the With tag. |
| |
Soundex? |
Returns a 4-5 digit integer number representing the Soundex code for the current string (or -1 if errors). The resulting number will always be less than 216 |
| |
Title? |
Capitalizes the first letter of each word in the string, all other letters are set to lower case (same as Capitalize?). |
| |
Trim? |
Trims all leading and trailing white characters from the string. |
| |
UC? |
Converts the string to upper case. This tag may also be used for force case-insensitive searches and comparisons. |
Description
The Str module performs various string functions. Many of the options can be chained as shown in the examples below. The Str module can be used without any tagged arguments to convert and concatenate any number of V4 points into a single string point on the Alpha dimension.
The resulting point will be a point on Dim:Alpha unless all component points of the string are of the same dimension and that dimension is an Alpha point type. When these two conditions are met the resulting point will be a point on that dimension.
This module also operates with BigText points. If the resulting string exceeds the allowed length of a V4 Alpha point then V4 will return a point of type BigText. The dimension will be either the dimension of the last BigText argument, or if none of the arguments were of that type then the Dim:Alpha dimension will be used (yes, a Dim:Alpha point of type BigText - go figure).
The nStr module is equivalent to {~Str()}.
Note that the UV4:none point is converted to an empty string (i.e. not formatted).
Examples
| |
Str("now is the time" UC?) |
NOW IS THE TIME |
| |
Str("Now is the time" Head::NOW) |
Logical:False |
| |
Str("Now is the time" UC? Head::NOW) |
Int:1 |
| |
Str("Now is the" UC? Head::(how about now)) |
Int:3 |
| |
Str("We the people" Begin::4 Length::3) |
the |
| |
Str("We the people" Begin::-6 End::-1) |
people |
| |
Str("We the people" Tail::6) |
people |
| |
Str("We the people" Tail::-4) |
the people |
| |
Str("We the people" Head::6) |
We the |
| |
Str("We the people" Head::-6) |
We the p |
| |
Str("We the people" ListOf::" " Trim?) |
("We" "the" "people") |
| |
Str("We the people" ListOf?) |
("W" "e" " " "t" "h" "e" " " "p" "e" "o" "p" "l" "e") |
| |
Str("We the people" ListOf::" " Trim? Head::2) |
("We" "the") |
| |
Str("In order to form" Has::the) |
Logical:No |
| |
Str("In order to form" Has::to) |
Int:10 |
| |
Str("INORDERTOFORM" Has::to) |
Logical:No |
| |
nStr("INORDERTOFORM" Has::to) |
Logical:Yes |
| |
Str("INORDERTOFORM" UC? Has::to) |
Int:8 |
| |
Str("Now is the time" Before::" ") |
Now |
| |
Str("Now is the time" Anchor::RHS Before::" ") |
Now is the |
| |
Str(x:"Now is the time" ListOf::" " Trim?) |
(x:"Now" x:"is" x:"the" x:"time") |
| |
Str(x:"Now is the " "time" ListOf::" " Trim?) |
("Now" "is" "the" "time") |
| |
Str("Now's the time" Literal::"'") |
'Now\'s the time' |
| |
Str("Now's the time" Escape::HTML Literal::"'") |
'Now's the time' |
| |
Str("Now is {the} time" Escape::none Literal::"{") |
{Now is {the}} time} |
| |
Str("nowxisxthe" Replace::"x" With::" ") |
now isxthe |
| |
Str("nowxisxthe" Replace::"x" Num? With::" ") |
now is the |
| |
Str("now is the time" RegExp::"( +)" Replace::1 Num? With::"|") |
now|is|the|time |
| |
Str("file.ext" RegExp::"^(.*)$" New::"copy ~1 f:~1") |
copy file.ext f:file.ext |
| |
Str("now is the time" Replace::((a x) (e x) (i xx) (o x) (u x)) |
nxw xxs thx txxmx |
| |
Str("now is the time" Break::(1 5 8 10)) |
("now " "is " "th" "e time") |
| |
Str("now is the time" Break::Int2:<5 10>) |
("now " "is the" " time") |
| |
Str("now is the time" All::"([A-Za-z]+)") |
(Int2:<1 3> Int2:<5 6> Int2:<8 10> Int2:<12 15>) |
| |
Str("now is the time!" Break::Str("now is the time!" All::"([A-Za-z]+)")) |
("" "now" " " "is" " " "the" " " "time" "!") |
| |
Str(Soundex::"ST JOHN") |
Alpha:"S532" |
| |
Str("Saint John" Soundex?) |
Int:19532 (integer equivalent of above) |
| |
Str("Today is /{Format(UDate:{now} Mask::'mmmm d, yyyy')}/" Evaluate::"/{") |
Today is February 12, 2005 |
| |
Str(XML::"a href='www.moo.com'" "Visit moo.com") |
<a href='www.moo.com'>Visit moo.com</a> |
| |
Str("abcdefg" Nth::Int:5,4,3) |
edc |
Sum - Sum a List of Numbers
Usage
Parameters
| |
resnum |
The resulting numerical point.The resulting dimension is either Int or Num depending on the actual sum. If the sum has a fractional part then the result is a point on the Num dimension, otherwise the result is an Int point. |
| |
list |
A list of numerical points. |
Description
This module sums its list of numbers.
Examples
| |
Sum(List(Int:1..10)) |
Int:55 |
| |
Sum((1 2 3 4 5.0)) |
Int:15 |
| |
Sum((1 2 3 4 5.1)) |
Num:15.1 |
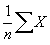
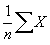
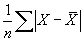
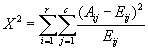

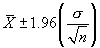 . If our sample is 100 apples with an average weight of 100 grams and a standard deviation of 1.8 then we can be 95% confident that the population mean is in the interval of
. If our sample is 100 apples with an average weight of 100 grams and a standard deviation of 1.8 then we can be 95% confident that the population mean is in the interval of 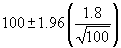 .
. 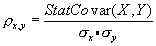
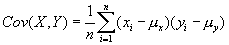

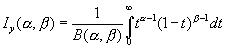 where y is
where y is 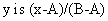
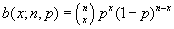 and the cumulative distribution function is
and the cumulative distribution function is 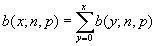
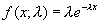 and the formula for the cumulative function is
and the formula for the cumulative function is 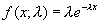
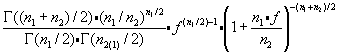 where n1 and n2 are the degrees of freedom.
where n1 and n2 are the degrees of freedom.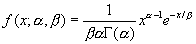
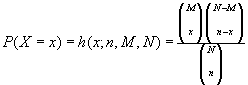
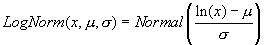
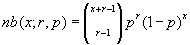
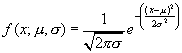
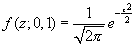
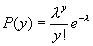 where lambda is the mean. The cumulative density function is given as
where lambda is the mean. The cumulative density function is given as 
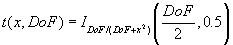
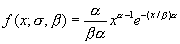
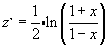
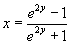

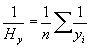
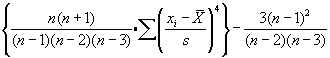
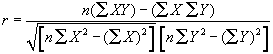
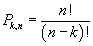
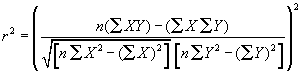
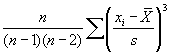
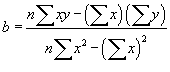
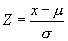
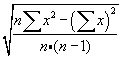
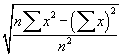
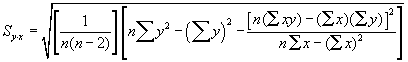
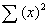
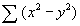

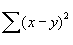
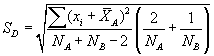 and
and 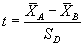 For unequal variance the following equation is used-
For unequal variance the following equation is used- 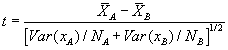 And for paired-
And for paired- 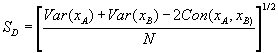 and
and